A role for K-ras in conferring resistance to the MEK inhibitor, CI-1040
- PMID: 15967111
- PMCID: PMC1501146
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.04532
A role for K-ras in conferring resistance to the MEK inhibitor, CI-1040
Abstract
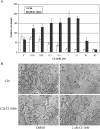
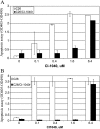
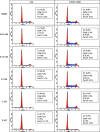
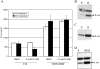
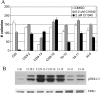
PD184352/CI-1040 is a potent and selective MEK1/2 inhibitor that represents the first MEK-targeted agent to enter clinical trials. Here, we report the development and molecular characterization of CI-1040 resistance in the murine colon 26 (C26) carcinoma cell line. The growth rate of the resistant line (C26/CI-1040r) in the presence of 2 microM CI-1040 is comparable to that of parental C26 cells in the absence of CI-1040. C26/CI-1040r cells are approximately 100-fold more resistant than the parental line to CI-1040 inhibition in soft agar and are less sensitive to the induction of apoptosis that normally occurs in response to CI-1040 treatment. K-ras expression is significantly elevated in C26/CI-1040r cells. We confirmed a causative role for K-ras in conferring resistance to CI-1040 by transfecting K-ras into parental C26 cells, whereupon an elevation in the levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 was observed in addition to resistance to CI-1040. Furthermore, an in vivo-derived MEK inhibitor-resistant line also shows increased K-ras expression. Our data suggest that increasing activated K-ras expression represents one potential mechanism by which tumor cells that initially are responsive to blockade of the MAP kinase pathway can overcome their sensitivity to MEK inhibition.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antitumor activity of pimasertib, a selective MEK 1/2 inhibitor, in combination with PI3K/mTOR inhibitors or with multi-targeted kinase inhibitors in pimasertib-resistant human lung and colorectal cancer cells.Int J Cancer. 2013 Nov;133(9):2089-101. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28236. Epub 2013 May 29. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23629727
-
Prolonged extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation during fibroblast growth factor 1- or heregulin beta1-induced antiestrogen-resistant growth of breast cancer cells is resistant to mitogen-activated protein/extracellular regulated kinase kinase inhibitors.Cancer Res. 2004 Jul 1;64(13):4637-47. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-2645. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15231676
-
Pharmacologic mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase/mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors interact synergistically with STI571 to induce apoptosis in Bcr/Abl-expressing human leukemia cells.Cancer Res. 2002 Jan 1;62(1):188-99. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11782377
-
Oncogenic K-ras confers SAHA resistance by up-regulating HDAC6 and c-myc expression.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 1;7(9):10064-72. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7134. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26848526 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic activity and heterogeneous acquired resistance of combined MDM2 and MEK inhibition in KRAS mutant cancers.Oncogene. 2017 Nov 23;36(47):6581-6591. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.258. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28783173 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhanced inhibition of ERK signaling by a novel allosteric MEK inhibitor, CH5126766, that suppresses feedback reactivation of RAF activity.Cancer Res. 2013 Jul 1;73(13):4050-4060. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3937. Epub 2013 May 10. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23667175 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to Molecularly Targeted Therapies in Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 5;13(5):1115. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051115. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical activity of the rational combination of selumetinib (AZD6244) in combination with vorinostat in KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer models.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Feb 15;18(4):1051-62. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1507. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22173548 Free PMC article.
-
Ras Dimer Formation as a New Signaling Mechanism and Potential Cancer Therapeutic Target.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016;16(5):391-403. doi: 10.2174/1389557515666151001152212. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26423697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of oncogenic driver mutations on feedback between the PI3K and MEK pathways in cancer cells.Biosci Rep. 2012 Aug;32(4):413-22. doi: 10.1042/BSR20120050. Biosci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22668349 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adjei AA. Blocking oncogenic Ras signaling for cancer therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:1062–1074. - PubMed
-
- Bos JL. ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:4682–4689. - PubMed
-
- Vojtek AB, Der CJ. Increasing complexity of the Ras signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:19925–19928. - PubMed
-
- Chong H, Vikis HG, Guan KL. Mechanisms of regulating the Raf kinase family. Cell Signal. 2003;15:463–469. - PubMed
-
- Cobb MH, Xu S, Hepler JE, Hutchison M, Frost J, Robbins DJ. Regulation of the MAP kinase cascade. Cell Mol Biol Res. 1994;40:253–256. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
