Stress granules and processing bodies are dynamically linked sites of mRNP remodeling
- PMID: 15967811
- PMCID: PMC2171635
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200502088
Stress granules and processing bodies are dynamically linked sites of mRNP remodeling
Abstract
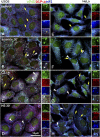
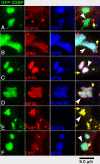
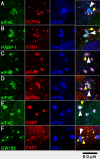
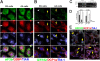
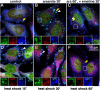
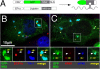
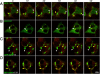
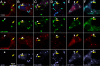
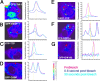
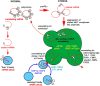
Stress granules (SGs) are cytoplasmic aggregates of stalled translational preinitiation complexes that accumulate during stress. GW bodies/processing bodies (PBs) are distinct cytoplasmic sites of mRNA degradation. In this study, we show that SGs and PBs are spatially, compositionally, and functionally linked. SGs and PBs are induced by stress, but SG assembly requires eIF2alpha phosphorylation, whereas PB assembly does not. They are also dispersed by inhibitors of translational elongation and share several protein components, including Fas-activated serine/threonine phosphoprotein, XRN1, eIF4E, and tristetraprolin (TTP). In contrast, eIF3, G3BP, eIF4G, and PABP-1 are restricted to SGs, whereas DCP1a and 2 are confined to PBs. SGs and PBs also can harbor the same species of mRNA and physically associate with one another in vivo, an interaction that is promoted by the related mRNA decay factors TTP and BRF1. We propose that mRNA released from disassembled polysomes is sorted and remodeled at SGs, from which selected transcripts are delivered to PBs for degradation.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson, P., and N. Kedersha. 2002. Stressful initiations. J. Cell Sci. 115:3227–3234. - PubMed
-
- Bolling, F., R. Winzen, M. Kracht, B. Bhebremedhin, B. Ritter, A. Wilhelm, K. Resch, and H. Holtmann. 2002. Evidence for general stabilization of mRNAs in response to UV light. Eur. J. Biochem. 269:5830–5839. - PubMed
-
- Chen, C.Y., R. Gherzi, S.E. Ong, E.L. Chan, R. Raijmakers, G.J. Pruijn, G. Stoecklin, C. Moroni, M. Mann, and M. Karin. 2001. AU binding proteins recruit the exosome to degrade ARE-containing mRNAs. Cell. 107:451–464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AR051472/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HL070819/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI033600/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033600/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL070819/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL52173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL032854/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK042394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI33600/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM066811/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI050167/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK42394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM 066811/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL32854/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR051472/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL032854/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK042394/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL052173/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI50167/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

