Difference in trafficking of brain-derived neurotrophic factor between axons and dendrites of cortical neurons, revealed by live-cell imaging
- PMID: 15969745
- PMCID: PMC1180452
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-6-42
Difference in trafficking of brain-derived neurotrophic factor between axons and dendrites of cortical neurons, revealed by live-cell imaging
Abstract
Background: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is sorted into a regulated secretory pathway of neurons, is supposed to act retrogradely through dendrites on presynaptic neurons or anterogradely through axons on postsynaptic neurons. Depending on which is the case, the pattern and direction of trafficking of BDNF in dendrites and axons are expected to be different. To address this issue, we analyzed movements of green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged BDNF in axons and dendrites of living cortical neurons by time-lapse imaging. In part of the experiments, the expression of BDNF tagged with cyan fluorescent protein (CFP) was compared with that of nerve growth factor (NGF) tagged with yellow fluorescent protein (YFP), to see whether fluorescent protein-tagged BDNF is expressed in a manner specific to this neurotrophin.
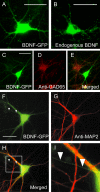
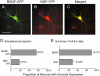
Results: We found that BDNF tagged with GFP or CFP was expressed in a punctated manner in dendrites and axons in about two-thirds of neurons into which plasmid cDNAs had been injected, while NGF tagged with GFP or YFP was diffusely expressed even in dendrites in about 70% of the plasmid-injected neurons. In neurons in which BDNF-GFP was expressed as vesicular puncta in axons, 59 and 23% of the puncta were moving rapidly in the anterograde and retrograde directions, respectively. On the other hand, 64% of BDNF-GFP puncta in dendrites did not move at all or fluttered back and forth within a short distance. The rest of the puncta in dendrites were moving relatively smoothly in either direction, but their mean velocity of transport, 0.47 +/- 0.23 (SD) microm/s, was slower than that of the moving puncta in axons (0.73 +/- 0.26 microm/s).
Conclusion: The present results show that the pattern and velocity of the trafficking of fluorescence protein-tagged BDNF are different between axons and dendrites, and suggest that the anterograde transport in axons may be the dominant stream of BDNF to release sites.
Figures


References
-
- Thoenen H. Neurotropins and neuronal plasticity. Science. 1995;270:593–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

