Dental disease in children with chronic illness
- PMID: 15970611
- PMCID: PMC1720486
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2004.058065
Dental disease in children with chronic illness
Abstract
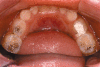
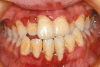
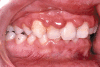
This article aims to raise awareness among paediatricians and specialist paediatric services that poor oral health, in particular children with chronic illness, is a major cause of morbidity and can be a risk factor for severe, even life threatening complications. Good oral health and dentition is important for efficient mastication, speaking and of course, cosmetically for smiling. If left untreated, dental caries can lead to pain and infection. Chronic infection around one or more teeth can result in damage to localised structures, such as the developing permanent teeth. Children who are medically compromised (such as being immunocompromised from disease and/or therapy) however are at increased risk of developing systemic complications from dental infections, which may prove fatal. We focus on the role of the general paediatrician in promoting the importance of good dental health for all children and in particular those children "at risk". We present preventive measures, evidence based where available, that may improve dental care and promote the role of paediatric dental services in the multidisciplinary management of chronic disease.
Figures
Comment in
-
The dental health of children with refractory epilepsy in a residential school.Arch Dis Child. 2005 Dec;90(12):1318. Arch Dis Child. 2005. PMID: 16301567 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
[The status of stomatologic prevention and therapy in children with chronic diseases].Arztl Jugendkd. 1991;82(2):103-6. Arztl Jugendkd. 1991. PMID: 1836934 German.
-
Building better oral health: a dental home for all Texans.Tex Dent J. 2008 Winter;Suppl:1-56. Tex Dent J. 2008. PMID: 19363885
-
Oral disease in children with Down syndrome: causes and prevention.Community Pract. 2010 Feb;83(2):18-21. Community Pract. 2010. PMID: 20222361
-
Assessment, management, and prevention of early childhood caries.J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2009 Jan;21(1):1-10. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7599.2008.00367.x. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2009. PMID: 19125889 Review.
-
Promoting oral health from birth through childhood: prevention of early childhood caries.MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs. 2008 Jan-Feb;33(1):17-23; quiz 24-5. doi: 10.1097/01.NMC.0000305652.01743.8d. MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs. 2008. PMID: 18158522 Review.
Cited by
-
Preventive dental care utilization and dental caries for Medicaid-enrolled adolescents in Oregon.J Public Health Dent. 2023 Jul;83(3):309-316. doi: 10.1111/jphd.12583. Epub 2023 Jul 31. J Public Health Dent. 2023. PMID: 37525392 Free PMC article.
-
Oral health care in children with haemophilia in Helsinki, Finland.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2013 Oct;14(5):339-43. doi: 10.1007/s40368-013-0090-z. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2013. PMID: 24068491
-
Effectiveness of Various Sensory Input Methods in Dental Health Education Among Blind Children- A Comparative Study.J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 Oct;9(10):ZC75-8. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/15499.6686. Epub 2015 Oct 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015. PMID: 26557623 Free PMC article.
-
ORO-FACIAL FASCIAL SPACE INFECTION IN A PAEDIATRIC GAMBIAN POPULATION: A REVIEW OF 93 CASES.J West Afr Coll Surg. 2018 Oct-Dec;8(4):1-23. J West Afr Coll Surg. 2018. PMID: 33553049 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric Liquid Medications and Dental Caries: A Narrative Review.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 23;8(7):e71115. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.71115. eCollection 2025 Jul. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40704323 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical