Monoclonal antibody A7-superparamagnetic iron oxide as contrast agent of MR imaging of rectal carcinoma
- PMID: 15970924
- PMCID: PMC2361484
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602668
Monoclonal antibody A7-superparamagnetic iron oxide as contrast agent of MR imaging of rectal carcinoma
Abstract
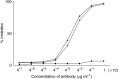
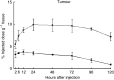
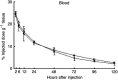
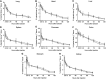
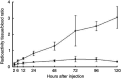
Superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO)-based colloid has been used clinically as a tissue-specific magnetic resonance contrast agent. We coupled monoclonal antibody A7 (Mab A7), which reacts specifically with human colorectal carcinoma, to Ferumoxides (SPIO) and examined the accumulation of this conjugate in xenografted tumours in nude mice. We examined in vitro immunoreactivity of Mab A7 coupled to Ferumoxides and its in vivo distribution in nude mice with human colorectal carcinoma. Magnetic resonance imaging of tumour-bearing nude mice was performed 72 h after injection of A7-Ferumoxides. A7-Ferumoxides retained binding activities that were nearly identical to intact Mab A7. More of the radiolabelled A7-Ferumoxides accumulated in the tumour than normal mouse IgG-Ferumoxides from 12 h onwards after injection (P<0.05). Both A7-Ferumoxides and normal mouse IgG-Ferumoxides disappeared from blood linearly over time. The accumulation levels in normal tissue decreased linearly over time but were lower than levels in tumours from 6 h. In magnetic resonance T2-weighted imaging of the tumour-bearing nude mice, signal intensity was reduced at the margin of the tumour by injection of A7-Ferumoxides. Mab A7 coupled to Ferumoxides is potentially suitable as a magnetic resonance contrast agent for detecting local recurrence of rectal carcinoma.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Monoclonal antibody A7 coupled to magnetic particles as a contrast enhancing agent for magnetic resonance imaging of human colorectal carcinoma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006 Jun;55(6):728-33. doi: 10.1007/s00262-005-0067-9. Epub 2005 Nov 5. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2006. PMID: 16273351 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal antibody conjugated to gadolinium as a contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging of human rectal carcinoma.J Surg Oncol. 2006 Aug 1;94(2):144-8. doi: 10.1002/jso.20411. J Surg Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16847923
-
Local administration of monoclonal antibody-drug conjugate: a new strategy to reduce the local recurrence of colorectal cancer.Cancer Res. 1992 Nov 15;52(22):6323-8. Cancer Res. 1992. PMID: 1423277
-
Molecular Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Human Colorectal Carcinoma (LoVo) Cells Using Novel Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide- Loaded Nanovesicles: In Vitro and in vivo Studies.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016;16(6):551-60. doi: 10.2174/1568009616666160603123616. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 27262319
-
Monoclonal antibody against antigen A7 coupled to ferromagnetic lignosite particles.2008 Nov 20 [updated 2008 Dec 17]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Nov 20 [updated 2008 Dec 17]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641309 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: promises for diagnosis and treatment of cancer.Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 2011;2(4):367-90. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 2011. PMID: 22199999 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional magnetic nanoparticles for targeted imaging and therapy.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008 Aug 17;60(11):1241-1251. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2008.03.014. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008. PMID: 18508157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of HSPG2 (Perlecan) as a Therapeutic Target in Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Sci Rep. 2019 Aug 28;9(1):12492. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48993-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31462656 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Nanotechnology in Targeting of Cancer Stem Cells: A Review.Int J Stem Cells. 2019 Jul 31;12(2):227-239. doi: 10.15283/ijsc19006. Int J Stem Cells. 2019. PMID: 31242721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo molecular targeting effects of anti-Sp17- ICG-Der-02 on hepatocellular carcinoma evaluated by an optical imaging system.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Mar 3;30(1):25. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-30-25. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21366930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adell G, Zhang H, Jansson A, Sun XF, Stal O, Nordenskjold B (2001) Decreased tumor cell proliferation as an indicator of the effect of preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50: 659–663 - PubMed
-
- Balzer JO, Luboldt W, Vogl TJ (2003) Importance of CT and MRI in the follow-up of patients with rectal cancer. Radiologie 43: 122–127 - PubMed
-
- Blomqvist L, Holm T, Goranson H, Jacobsson H, Ohlsen H, Larsson SA (1996) MR imaging, CT and CEA scintigraphy in the diagnosis of local recurrence of rectal carcinoma. Acta Radiol 37: 779–784 - PubMed
-
- Clement O, Frija G, Chambon C, Schouman-Clayes E, Mosnier JF, Poupon MF, Balkau B (1991) Liver tumors in cirrhosis: experimental study with SPIO-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 180: 31–36 - PubMed
-
- Frykholm GJ, Pahlman L, Glimelius B (2001) Combined chemo- and radiotherapy vs radiotherapy vs radiotherapy alone in the treatment of primary, nonresectable adenocarcinoma of the rectum. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 50: 427–434 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

