Derivation of multipotent mesenchymal precursors from human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 15971941
- PMCID: PMC1160574
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0020161
Derivation of multipotent mesenchymal precursors from human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Background: Human embryonic stem cells provide access to the earliest stages of human development and may serve as a source of specialized cells for regenerative medicine. Thus, it becomes crucial to develop protocols for the directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells into tissue-restricted precursors.
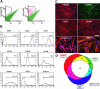
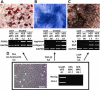
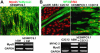
Methods and findings: Here, we present culture conditions for the derivation of unlimited numbers of pure mesenchymal precursors from human embryonic stem cells and demonstrate multilineage differentiation into fat, cartilage, bone, and skeletal muscle cells.
Conclusion: Our findings will help to elucidate the mechanism of mesoderm specification during embryonic stem cell differentiation and provide a platform to efficiently generate specialized human mesenchymal cell types for future clinical applications.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Reubinoff BE, Itsykson P, Turetsky T, Pera MF, Reinhartz E, et al. Neural progenitors from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2001;19:1134–1140. - PubMed
-
- Zhang SC, Wernig M, Duncan ID, Brustle O, Thomson JA. In vitro differentiation of transplantable neural precursors from human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2001;19:1129–1133. - PubMed
-
- Sottile V, Thomson A, McWhir J. In vitro osteogenic differentiation of human ES cells. Cloning Stem Cells. 2003;5:149–155. - PubMed
-
- Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal RK, Douglas R, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284:143–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

