Alveolar macrophages regulate neutrophil recruitment in endotoxin-induced lung injury
- PMID: 15972102
- PMCID: PMC1188075
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-6-61
Alveolar macrophages regulate neutrophil recruitment in endotoxin-induced lung injury
Abstract
Background: Alveolar macrophages play an important role during the development of acute inflammatory lung injury. In the present study, in vivo alveolar macrophage depletion was performed by intratracheal application of dichloromethylene diphosphonate-liposomes in order to study the role of these effector cells in the early endotoxin-induced lung injury.
Methods: Lipopolysaccharide was applied intratracheally and the inflammatory reaction was assessed 4 hours later. Neutrophil accumulation and expression of inflammatory mediators were determined. To further analyze in vivo observations, in vitro experiments with alveolar epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages were performed.
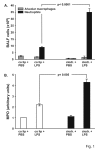
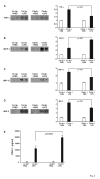
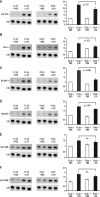
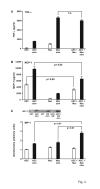
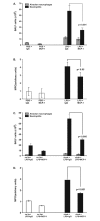
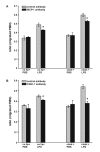
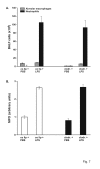
Results: A 320% increase of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was observed in macrophage-depleted compared to macrophage-competent lipopolysaccharide-animals. This neutrophil recruitment was also confirmed in the interstitial space. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 concentration in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was significantly increased in the absence of alveolar macrophages. This phenomenon was underlined by in vitro experiments with alveolar epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages. Neutralizing monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in the airways diminished neutrophil accumulation.
Conclusion: These data suggest that alveolar macrophages play an important role in early endotoxin-induced lung injury. They prevent neutrophil influx by controlling monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 production through alveolar epithelial cells. Alveolar macrophages might therefore possess robust anti-inflammatory effects.
Figures
References
-
- Beck-Schimmer B, Schimmer RC, Warner RL, Schmal H, Nordblom G, Flory CM, Lesch ME, Friedl HP, Schrier DJ, Ward PA. Expression of lung vascular and airway ICAM-1 after exposure to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997;17:344–352. - PubMed
-
- Li XY, Donaldson K, MacNee W. Lipopolysaccharide-induced alveolar epithelial permeability: the role of nitric oxide. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:1027–1033. - PubMed
-
- Madjdpour C, Oertli B, Ziegler U, Bonvini JM, Pasch T, Beck-Schimmer B. Lipopolysaccharide induces functional ICAM-1 expression in rat alveolar epithelial cells in vitro. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000;278:L572–9. - PubMed
-
- Sibille Y, Reynolds HY. Macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils in lung defense and injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990;141:471–501. - PubMed
-
- Monton C, Torres A. Lung inflammatory response in pneumonia. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 1998;53:56–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

