NF-kappaB activation and potentiation of proinflammatory responses by the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein
- PMID: 15972330
- PMCID: PMC1166591
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409873102
NF-kappaB activation and potentiation of proinflammatory responses by the Helicobacter pylori CagA protein
Abstract
The Helicobacter pylori immunodominant protein, CagA, is associated with severe gastritis and carcinoma. Injection of CagA into gastric epithelial cells by type IV secretion leads to actin-cytoskeletal rearrangements and cell scattering. CagA has been reported to have no role in the induction of transcription factor NF-kappaB and IL-8, which are crucial determinants for chronic inflammation. Here, we provide several lines of evidence showing that CagA is able to induce IL-8 in a time- and strain-dependent manner. We also show that by exchanging specific cagA genes, high IL-8-inducing H. pylori strains could be converted into low inducing strains and vice versa. Our results suggest that IL-8 release induced by CagA occurs via a Ras-->Raf-->Mek-->Erk-->NF-kappaB signaling pathway in a Shp-2- and c-Met-independent manner. Thus, CagA is a multifunctional protein capable of effecting both actin remodeling and potentiation of chemokine release.
Figures
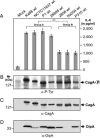
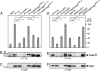
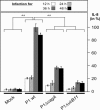



References
-
- Medzhitov, R. (2001) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 1, 135-145. - PubMed
-
- Akira, S. (2003) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15, 5-11. - PubMed
-
- Beutler, B. (2004) Nature 430, 257-263. - PubMed
-
- Girardin, S. E., Sansonetti, P. J. & Philpott, D. J. (2002) Trends Microbiol. 10, 193-199. - PubMed
-
- Viala, J., Chaput, C., Boneca, I. G., Cardona, A., Girardin, S. E., Moran, A. P., Athman, R., Memet, S., Huerre, M. R., Coyle, A. J., et al. (2004) Nat. Immunol. 5, 1166-1174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

