Characterization of a human monoclonal antibody against Shiga toxin 2 expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells
- PMID: 15972493
- PMCID: PMC1168570
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.7.4054-4061.2005
Characterization of a human monoclonal antibody against Shiga toxin 2 expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells
Abstract
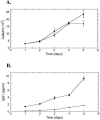
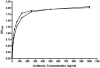
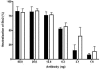
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections can often lead to the development of hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS) in a small percentage of infected humans. Patients with HUS receive only supportive treatment as the benefit of antibiotic therapy remains uncertain. We have previously reported the generation and preclinical evaluation of neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies (HuMAbs) against the Shiga toxins (Stx). In this paper, we describe the expression in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells of 5C12 HuMAb, which is directed against the A subunit of Stx2. The cDNAs of the light and heavy chain immunoglobulin (Ig) variable regions of 5C12 HuMAb were isolated and cloned into an expression vector containing human IgG1 constant regions. The vector was transfected into CHO cells, and transfectants secreting Stx2-specific antibody were screened by an Stx2-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The CHO-produced recombinant 5C12 (r5C12) showed similar specificity and binding affinity to Stx2 as the parent hybridoma-produced 5C12. More significantly, the r5C12 displayed the same neutralizing activity as the parent 5C12 in vitro and in vivo. In the mouse toxicity model, both antibodies significantly and equally prolonged survival at a dose of 0.312 microg/mouse. The data showed that since r5C12, produced in CHO cells, was equally effective as the parent 5C12, it is our choice candidate as a potential prophylactic or therapeutic agent against hemolytic-uremic syndrome.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human Stx2-specific monoclonal antibodies prevent systemic complications of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection.Infect Immun. 2002 Feb;70(2):612-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.2.612-619.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11796590 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Fab and F(ab')2 fragments and isotype variants of a recombinant human monoclonal antibody against Shiga toxin 2.Infect Immun. 2010 Mar;78(3):1376-82. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00867-09. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20086088 Free PMC article.
-
Biodistribution and elimination kinetics of systemic Stx2 by the Stx2A and Stx2B subunit-specific human monoclonal antibodies in mice.BMC Immunol. 2012 Jun 1;13:27. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-13-27. BMC Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22655967 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody therapy in the management of shiga toxin-induced hemolytic uremic syndrome.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004 Oct;17(4):926-41, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/CMR.17.4.926-941.2004. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15489355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Antibodies Against Shiga Toxins: Trends and Perspectives.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Feb 10;12:825856. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.825856. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35223548 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antibody against TcdB, but not TcdA, prevents development of gastrointestinal and systemic Clostridium difficile disease.J Infect Dis. 2013 Jan 15;207(2):323-30. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis669. Epub 2012 Nov 2. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23125448 Free PMC article.
-
Shiga toxin 2-specific but not shiga toxin 1-specific human monoclonal antibody protects piglets challenged with enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli producing shiga toxin 1 and shiga toxin 2.J Infect Dis. 2010 Apr 1;201(7):1081-3. doi: 10.1086/651198. J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20196656 Free PMC article.
-
Fusion expression and immunogenicity of EHEC EspA-Stx2Al protein: implications for the vaccine development.J Microbiol. 2009 Aug;47(4):498-505. doi: 10.1007/s12275-009-0116-8. Epub 2009 Sep 9. J Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19763426
-
Shiga toxin pathogenesis: kidney complications and renal failure.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012;357:105-36. doi: 10.1007/82_2011_172. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 21983749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Multi-Specific DARPin Potently Neutralizes Shiga Toxin 2 via Simultaneous Modulation of Both Toxin Subunits.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Sep 27;9(10):511. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9100511. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alt, F. W., R. E. Kellems, J. R. Bertino, and R. T. Schimke. 1978. Selective amplification of dihydrofolate reductase genes in methotrexate-resistant variants of cultured murine cells. J. Biol. Chem. 252:1357-1370. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, D. C., and L. Krummen. 2002. Recombinant protein expression for therapeutic applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 13:117-123. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, G. D., P. C. Rowe, P. Goodyer, E. Orrbine, T. P. Klassen, G. Wells, A. MacKenzie, H. Lior, C. Blanchard, F. Auclair, et al. 1995. A phase I study of chemically synthesized verotoxin (Shiga-like toxin) Pk-trisaccharide receptors attached to chromosorb for preventing hemolytic-uremic syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 171:1042-1045. - PubMed
-
- Arunachalam, B., S. Ghosh, G. P. Talwar, and R. Raghupathy. 1992. A single human monoclonal antibody that confers total protection from tetanus. Hybridoma 11:165-179. - PubMed
-
- Banatvala, N. P., P. M. Griffin, K. D. Greene, T. J. Barrett, W. F. Bibb, J. H. Green, and J. G. Wells. 2001. The United States National Prospective Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome Study: microbiologic, serologic, clinical, and epidemiologic findings. J. Infect. Dis. 183:1063-1070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

