Identification, cloning, and expression of the CAMP-like factor autotransporter gene (cfa) of Bartonella henselae
- PMID: 15972511
- PMCID: PMC1168562
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.7.4205-4213.2005
Identification, cloning, and expression of the CAMP-like factor autotransporter gene (cfa) of Bartonella henselae
Abstract
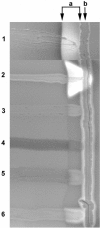
The CAMP reaction was first described by Christie et al. (R. Christie, N. E. Atkins, and E. Munch-Petersen, Aust. J. Exp. Biol. 22:197-200, 1944) as the synergistic lysis of sheep red blood cells by Staphylococcus aureus sphingomyelinase and CAMP factor (cohemolysin), a secreted protein from group B streptococci. We observed a CAMP-like reaction when Bartonella henselae was grown in close proximity to S. aureus on 5% sheep blood agar. This study describes the cloning, sequencing, and characterization of a CAMP-like factor autotransporter gene (cfa) from B. henselae. A cosmid library of B. henselae ATCC 49793 was constructed using SuperCos1 in Escherichia coli XL1-Blue MR. Cosmids were screened for the CAMP reaction, and a quantitative cohemolysis microtiter assay was developed using purified sphingomyelinase. Cosmid clones with the strongest cohemolytic reaction had similar restriction enzyme patterns. A DNA fragment that expressed the cohemolysin determinant was subcloned in a 7,200-bp StuI-BamHI fragment which contained a 6,024-bp open reading frame. The deduced amino acid sequence showed homology to the family of autotransporters. The autotransporters are a group of proteins that mediate their own export through the outer membrane. They contain an N-terminal passenger region, the alpha-domain, and a C-terminal transporter region, the beta-domain. The alpha-domain contained four, nearly identical 42-amino-acid repeats and showed homology to the family of RTX (repeat in toxin) hemolysins. The concentrated supernatant of the recombinant strain expressed a protein with a molecular mass of 180 kDa on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis consistent with the calculated molecular weight of the secreted alpha-domain. In conclusion, we have characterized a novel secreted cohemolysin autotransporter protein of B. henselae.
Figures


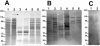
Similar articles
-
Characterization of an immunogenic outer membrane autotransporter protein, Arp, of Bartonella henselae.Infect Immun. 2007 Nov;75(11):5255-63. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00533-07. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17785470 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of CAMP cohemolysin as a potential virulence factor of Riemerella anatipestifer.J Bacteriol. 2002 Apr;184(7):1932-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.7.1932-1939.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 11889100 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, cloning, and expression of the CAMP factor gene (cfa) of group A streptococci.Infect Immun. 1999 Sep;67(9):4725-31. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.9.4725-4731.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10456923 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and expression of a cohemolysin, the CAMP factor of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae.Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2050-6. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2050-2056.1989. Infect Immun. 1989. PMID: 2659534 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of Bartonella-like isolates at the species level by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism in the citrate synthase gene.J Clin Microbiol. 1995 Jul;33(7):1797-803. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.7.1797-1803.1995. J Clin Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 7545181 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pestilence, persistence and pathogenicity: infection strategies of Bartonella.Future Microbiol. 2009 Aug;4(6):743-58. doi: 10.2217/fmb.09.41. Future Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19659429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the Bartonella autotransporter CFA as a protective antigen and hypervariable target of neutralizing antibodies in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Jun 21;119(25):e2202059119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2202059119. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35714289 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomics of culture isolates and insect tissue illuminate the evolution of Wolbachia, Rickettsia and Bartonella symbionts in Ctenocephalides spp. fleas.Microb Genom. 2023 Jul;9(7):mgen001045. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001045. Microb Genom. 2023. PMID: 37399133 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of an immunogenic outer membrane autotransporter protein, Arp, of Bartonella henselae.Infect Immun. 2007 Nov;75(11):5255-63. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00533-07. Epub 2007 Sep 4. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17785470 Free PMC article.
-
Autoprocessing of the Escherichia coli AIDA-I autotransporter: a new mechanism involving acidic residues in the junction region.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jun 19;284(25):17340-17351. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.010108. Epub 2009 Apr 27. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19398552 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. L. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen, J. D., H. Nielsen, G. Von Heijne, and S. Brunak. 2004. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 340:783-795. - PubMed
-
- Bullock, W. O., J. M. Fernández, and J. M. Short. 1987. XL1-Blue: a high efficiency plasmid transforming recA Escherichia coli strain with beta-galactosidase selection. BioTechniques 4:376-378.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

