Extracellular cyclophilins contribute to the regulation of inflammatory responses
- PMID: 15972687
- PMCID: PMC2862457
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.1.517
Extracellular cyclophilins contribute to the regulation of inflammatory responses
Abstract
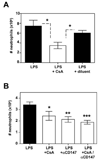
The main regulators of leukocyte trafficking during inflammatory responses are chemokines. However, another class of recently identified chemotactic agents is extracellular cyclophilins, the proteins mostly known as receptors for the immunosuppressive drug, cyclosporine A. Cyclophilins can induce leukocyte chemotaxis in vitro and have been detected at elevated levels in inflamed tissues, suggesting that they might contribute to inflammatory responses. We recently identified CD147 as the main signaling receptor for cyclophilin A. In the current study we examined the contribution of cyclophilin-CD147 interactions to inflammatory responses in vivo using a mouse model of acute lung injury. Blocking cyclophilin-CD147 interactions by targeting CD147 (using anti-CD147 Ab) or cyclophilin (using nonimmunosuppressive cyclosporine A analog) reduced tissue neutrophilia by up to 50%, with a concurrent decrease in tissue pathology. These findings are the first to demonstrate the significant contribution of cyclophilins to inflammatory responses and provide a potentially novel approach for reducing inflammation-mediated diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preferential chemotaxis of activated human CD4+ T cells by extracellular cyclophilin A.J Leukoc Biol. 2007 Sep;82(3):613-8. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0506317. Epub 2007 May 31. J Leukoc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17540735 Free PMC article.
-
Dealing with the family: CD147 interactions with cyclophilins.Immunology. 2006 Mar;117(3):301-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02316.x. Immunology. 2006. PMID: 16476049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cyclophilin-CD147 interactions: a new target for anti-inflammatory therapeutics.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Jun;160(3):305-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04115.x. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20345978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel approach to inhibit asthma-mediated lung inflammation using anti-CD147 intervention.J Immunol. 2006 Oct 1;177(7):4870-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.7.4870. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16982929 Free PMC article.
-
A cell-impermeable cyclosporine A derivative reduces pathology in a mouse model of allergic lung inflammation.J Immunol. 2010 Dec 15;185(12):7663-70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001707. Epub 2010 Nov 5. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 21057089 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cyclophilins as modulators of viral replication.Viruses. 2013 Jul 11;5(7):1684-701. doi: 10.3390/v5071684. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 23852270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Considerations of the effects of commonly investigated drugs for COVID-19 in the cholesterol synthesis pathway.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;22(8):947-952. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2021.1897104. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33703986 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Contribution of cyclophilin A to the regulation of inflammatory processes in rheumatoid arthritis.J Clin Immunol. 2010 Jan;30(1):24-33. doi: 10.1007/s10875-009-9329-1. Epub 2009 Sep 30. J Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 19789967
-
Basigin-mediated gene expression changes in mouse uterine stromal cells during implantation.Endocrinology. 2009 Feb;150(2):966-76. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-0571. Epub 2008 Oct 1. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 18832103 Free PMC article.
-
EMMPRIN-CypA contributes to the inflammatory processes in human periodontitis through infiltrating CD68+ inflammatory cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Aug 1;11(8):3828-3834. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31949770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin ZG, Melaragno MG, Liao DF, Yan C, Haendeler J, Suh YA, Lambeth JD, Berk BC. Cyclophilin A is a secreted growth factor induced by oxidative stress. Circ. Res. 2000;87:789–796. - PubMed
-
- Seko Y, Fujimura T, Taka H, Mineki R, Murayama K, Nagai R. Hypoxia followed by reoxygenation induces secretion of cyclophilin A from cultured rat cardiac myocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004;317:162–168. - PubMed
-
- Tegeder I, Schumacher A, John S, Geiger H, Geisslinger G, Bankg H, Brune K. Elevated serum cyclophilin levels in patients with severe sepsis. J. Clin. Immunol. 1997;17:380–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

