Restoration of normal distensive characteristics of the esophagogastric junction after fundoplication
- PMID: 15973100
- PMCID: PMC1357703
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000167868.44211.f0
Restoration of normal distensive characteristics of the esophagogastric junction after fundoplication
Abstract
Objective: To study the mechanical characteristics of the esophagogastric junction (EGJ) of postfundoplication patients and compare them with previously reported data on normal subjects and GERD patients.
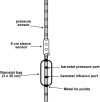
Methods: Eight normal subjects, 9 GERD patients, and 8 fundoplication patients were studied with concurrent manometry, fluoroscopy, and stepwise controlled barostat distention of the EGJ. The minimal barostat pressure required to open the EGJ during the interswallow period was determined. Thereafter, barium swallows were imaged in 5-mm Hg increments of intrabag pressure. EGJ diameter and length were measured at each pressure during deglutitive relaxation.
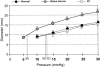
Results: EGJ opening diameter during deglutitive relaxation was on average 0.5 cm greater in GERD patients compared with normal subjects and fundoplication patients (P < 0.05). EGJ opening pressure and opening diameter were comparable between normal subjects and fundoplication patients; however, the EGJ length was 32% longer in fundoplication patients.
Conclusions: Fundoplication restores distensibility of the EGJ to a level similar to normal subjects. Since trans-EGJ flow is related to EGJ length and EGJ diameter, these findings suggest that retrograde flow through the EGJ would be decreased by both a reduction in diameter and an increase in length of the EGJ.
Figures


Comment in
-
Geometry and biomechanics of the esophagogastric junction: implications for antireflux surgery.Ann Surg. 2006 Feb;243(2):288; author reply 288-9. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000198342.20401.74. Ann Surg. 2006. PMID: 16432367 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Pandolfino JE, Shi G, Manka M, et al. EGJ opening with hiatal hernia: lower pressure threshold, wider diameter. Gastroenterology. 2000;118:A860.
-
- Kahrilas PJ, Lin S, Manka M, et al. Esophagogastric junction pressure topography after fundoplication. Surgery. 2000;127:200–208. - PubMed
-
- Whitehead WE, Delvaux M. Standardization of barostat procedures for testing smooth muscle tone and sensory thresholds in the gastrointestinal tract: the Working Team of Glaxo-Wellcome Research, UK. Dig Dis Sci. 1997;42:223–241. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Parashar VK, Mittal RK. Asymmetry of lower esophageal sphincter pressure: is it related to the muscle thickness or its shape? Am J Physiol. 1997;272:G1509–G1517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

