Regulation of hepatic metabolic pathways by the orphan nuclear receptor SHP
- PMID: 15973435
- PMCID: PMC1176456
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600728
Regulation of hepatic metabolic pathways by the orphan nuclear receptor SHP
Abstract
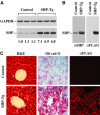
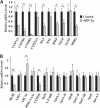
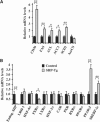
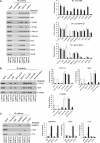
SHP (small heterodimer partner) is an important component of the feedback regulatory cascade, which controls the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids. In order to identify the bona fide molecular targets of SHP, we performed global gene expression profiling combined with chromatin immunoprecipitation assays in transgenic mice constitutively expressing SHP in the liver. We demonstrate that SHP affects genes involved in diverse biological pathways, and in particular, several key genes involved in consecutive steps of cholesterol degradation, bile acid conjugation, transport and lipogenic pathways. Sustained expression of SHP leads to the depletion of hepatic bile acid pool and a concomitant accumulation of triglycerides in the liver. The mechanism responsible for this phenotype includes SHP-mediated direct repression of downstream target genes and the bile acid sensor FXRalpha, and an indirect activation of PPARgamma and SREBP-1c genes. We present evidence for the role of altered chromatin configurations in defining distinct gene-specific mechanisms by which SHP mediates differential transcriptional repression. The multiplicity of genes under its control suggests that SHP is a pleiotropic regulator of diverse metabolic pathways.
Figures

References
-
- Bae Y, Kemper JK, Kemper B (2004) Repression of CAR-mediated transactivation of CYP2B genes by the orphan nuclear receptor, short heterodimer partner (SHP). DNA Cell Biol 23: 81–91 - PubMed
-
- Chiang JY (2002) Bile acid regulation of gene expression: roles of nuclear hormone receptors. Endocr Rev 23: 443–463 - PubMed
-
- Chiang JY (2004) Regulation of bile acid synthesis: pathways, nuclear receptors, and mechanisms. J Hepatol 40: 539–551 - PubMed
-
- del Castillo-Olivares A, Campos JA, Pandak WM, Gil G (2004) The role of alpha1-fetoprotein transcription factor/LRH-1 in bile acid biosynthesis: a known nuclear receptor activator that can act as a suppressor of bile acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 279: 16813–16821 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

