Influence of CO2 pneumoperitoneum on intracellular pH and signal transduction in cancer cells
- PMID: 15973767
- PMCID: PMC1389799
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.2005.B0650
Influence of CO2 pneumoperitoneum on intracellular pH and signal transduction in cancer cells
Abstract
Object: The authors studied the influence of CO(2) pneumoperitoneum on intracellular pH and signal transduction arising from cancer cell multiplication in laparoscopic tumor operation.
Method: They set up a simulation of pneumoperitoneum under different CO(2) pressure, and then measured the variation of intracellular pH (pHi) at different time and the activity of protein kinase C (PKC) and protein phosphatase 2a (PP2a) at the end of the pneumoperitoneum. After 1 week, the concentration of cancer cells in the culture medium was calculated.
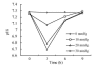
Result: When the pressure of CO(2) pneumoperitoneum was 0, 10, 20, 30 mmHg respectively, the average pHi was 7.273, 7.075, 6.783, 6.693 at the end of the pneumoperitoneum; PKC activity was 159.4, 168.5, 178.0, 181.6 nmol/(g.min) and PP2a was 4158.3, 4066.9, 3984.0, 3878.5 nmol/(g.min) respectively. After 1 week, the cancer cells concentration was 2.15 x 10(5), 2.03 x 10(5), 2.20 x 10(5), 2.18 x 10(5) L(-1).
Conclusion: CO(2) pneumoperitoneum could promote acidosis in cancer cells, inducing the activation of protein kinase C and deactivation of protein phosphatase 2a, but it could not accelerate the mitosis rate of the cancer cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effects of different CO2 pressure pneumoperitoneum on the migration and cytoskeleton in gastric cancer cells].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008 Sep;11(5):454-7. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 18803049 Chinese.
-
[Effect of carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum-laparoscopic surgery on tumor seeding and metastases in endometrial cancer].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2008 Feb;33(2):130-7. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2008. PMID: 18326907 Chinese.
-
Hyperthermic carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum reinforces the inhibition of 5-FU on the proliferation and invasion of colon cancer.Oncol Rep. 2017 Jan;37(1):492-500. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5229. Epub 2016 Nov 8. Oncol Rep. 2017. PMID: 27840981
-
Effects of adding small amounts of oxygen to a carbon dioxide-pneumoperitoneum of increasing pressure in rabbit ventilation models.Fertil Steril. 2009 Aug;92(2):778-84. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.07.019. Epub 2008 Sep 27. Fertil Steril. 2009. PMID: 18823885
-
Sublethal levels of oxidant stress stimulate multiple serine/threonine kinases and suppress protein phosphatases in Jurkat T cells.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995 May 10;319(1):23-35. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1995.1263. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1995. PMID: 7771789
Cited by
-
Effects of CO₂ pneumoperitoneum on the expression of thymidine kinase 1 and Ki67 in colorectal carcinoma cells.Surg Endosc. 2014 Oct;28(10):2863-70. doi: 10.1007/s00464-014-3539-1. Epub 2014 May 23. Surg Endosc. 2014. PMID: 24853840
References
-
- Abu-Rustum NR, Sonoda Y, Chi DS, Teoman H, Dizon DS, Venkatraman E, Barakat RR. The Effects of CO2 pneumoperitoneum on the survival of women with persistent metastatic ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2003;90:431–434. - PubMed
-
- Abu-Rustum NR, Rhee EH, Chi DS, Sonoda Y, Gemignani G, Barakat RR. Subcutaneous tumor implantation after laparoscopic procedures in women with malignant disease. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;103(3):480–487. - PubMed
-
- Cataldo PA. Wound metastasis after laparoscopy with different insufflation gases. Diseases of the Colon & Rectum. 1998;41(12):1595–1596.
-
- Celik V, Salihoglu Z, Demiroluk S, Unal E, Yavuz N, Karaca S, Carkman S, Demiroluk O. Effect of intra-abdominal pressure level on gastric intramucosal pH during pneumoperitoneum. Surgical Laparoscopy, Endoscopy & Percutaneous Techniques. 2004;14(5):247–249. - PubMed
-
- Hirabayashi Y, Yamaguchi K, Shiraishi N, Adachi Y, Kitamura H, Kitano S. Development of port-site metastasis after pneumoperitoneum. Surgical Endoscopy. 2002;16(5):864–868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical