Inhibition of Pkhd1 impairs tubulomorphogenesis of cultured IMCD cells
- PMID: 15975909
- PMCID: PMC1196347
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-11-1019
Inhibition of Pkhd1 impairs tubulomorphogenesis of cultured IMCD cells
Abstract
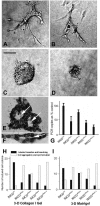
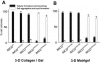
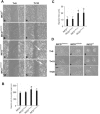
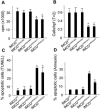
Fibrocystin/polyductin (FPC), the gene product of PKHD1, is responsible for autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). This disease is characterized by symmetrically large kidneys with ectasia of collecting ducts. In the kidney, FPC predominantly localizes to the apical domain of tubule cells, where it associates with the basal bodies/primary cilia; however, the functional role of this protein is still unknown. In this study, we established stable IMCD (mouse inner medullary collecting duct) cell lines, in which FPC was silenced by short hairpin RNA inhibition (shRNA). We showed that inhibition of FPC disrupted tubulomorphogenesis of IMCD cells grown in three-dimensional cultures. Pkhd1-silenced cells developed abnormalities in cell-cell contact, actin cytoskeleton organization, cell-ECM interactions, cell proliferation, and apoptosis, which may be mediated by dysregulation of extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling. These alterations in cell function in vitro may explain the characteristics of ARPKD phenotypes in vivo.
Figures





References
-
- Ambros, V. (2004). The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431, 350-355. - PubMed
-
- An, J., Chen, Y., Huang, Z. (2004). Critical upstream signals of cytochrome C release induced by a novel bcl-2 inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 19133-19140. - PubMed
-
- Balda, M. S., and Matter, K. (2003). Epithelial cell adhesion and the regulation of gene expression. Trends Cell Biol. 13, 310-318. - PubMed
-
- Berridge, M. V., Tan, A. S., McCoy, K. D., and Wang, R. (1996). The biochemical and cellular basis of cell proliferation assays that use tetrazolium salts. Biochemica 4, 12-20.
-
- Boletta, A., Qian, F., Onuchic, L. F., Bhunia, A. K., Phakdeekitcharoen, B., Hanaoka, K., Guggino, W., Monaco, L., Germino, G. G. (2002). Polycycstin-1, the gene product of PKD1, induces resistance to apoptosis and spontaneous tubulogenesis in MDCK cells. Mol. Cell 6, 1267-1273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

