GLUT1CBP(TIP2/GIPC1) interactions with GLUT1 and myosin VI: evidence supporting an adapter function for GLUT1CBP
- PMID: 15975910
- PMCID: PMC1196329
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e04-11-0978
GLUT1CBP(TIP2/GIPC1) interactions with GLUT1 and myosin VI: evidence supporting an adapter function for GLUT1CBP
Abstract
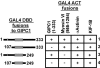
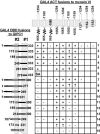
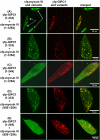
We identified a novel interaction between myosin VI and the GLUT1 transporter binding protein GLUT1CBP(GIPC1) and first proposed that as an adapter molecule it might function to couple vesicle-bound proteins to myosin VI movement. This study refines the model by identifying two myosin VI binding domains in the GIPC1 C terminus, assigning respective oligomerization and myosin VI binding functions to separate N- and C-terminal domains, and defining a central region in the myosin VI tail that binds GIPC1. Data further supporting the model demonstrate that 1) myosin VI and GIPC1 interactions do not require a mediating protein; 2) the myosin VI binding domain in GIPC1 is necessary for intracellular interactions of GIPC1 with myosin VI and recruitment of overexpressed myosin VI to membrane structures, but not for the association of GIPC1 with such structures; 3) GIPC1/myosin VI complexes coordinately move within cellular extensions of the cell in an actin-dependent and microtubule-independent manner; and 4) blocking either GIPC1 interactions with myosin VI or GLUT1 interactions with GIPC1 disrupts normal GLUT1 trafficking in polarized epithelial cells, leading to a reduction in the level of GLUT1 in the plasma membrane and concomitant accumulation in internal membrane structures.
Figures


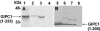


Similar articles
-
Protein interactions with the glucose transporter binding protein GLUT1CBP that provide a link between GLUT1 and the cytoskeleton.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Apr;10(4):819-32. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.4.819. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10198040 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin VI: two distinct roles in endocytosis.J Cell Sci. 2003 Sep 1;116(Pt 17):3453-61. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00669. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12893809 Review.
-
Structure analyses reveal a regulated oligomerization mechanism of the PlexinD1/GIPC/myosin VI complex.Elife. 2017 May 24;6:e27322. doi: 10.7554/eLife.27322. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28537552 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF-mediated neurotransmission relies upon a myosin VI motor complex.Nat Neurosci. 2006 Aug;9(8):1009-18. doi: 10.1038/nn1730. Epub 2006 Jul 2. Nat Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16819522
-
Myosin VI and its cargo adaptors - linking endocytosis and autophagy.J Cell Sci. 2013 Jun 15;126(Pt 12):2561-70. doi: 10.1242/jcs.095554. Epub 2013 Jun 18. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23781020 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neural tube closure requires the endocytic receptor Lrp2 and its functional interaction with intracellular scaffolds.Development. 2021 Jan 26;148(2):dev195008. doi: 10.1242/dev.195008. Development. 2021. PMID: 33500317 Free PMC article.
-
Dematin and adducin provide a novel link between the spectrin cytoskeleton and human erythrocyte membrane by directly interacting with glucose transporter-1.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 23;283(21):14600-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707818200. Epub 2008 Mar 17. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18347014 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases endocytosis in endothelium: biology and signaling.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Sep;34(9):1831-7. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303217. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24925972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T6BP and NDP52 are myosin VI binding partners with potential roles in cytokine signalling and cell adhesion.J Cell Sci. 2007 Aug 1;120(Pt 15):2574-85. doi: 10.1242/jcs.007005. Epub 2007 Jul 17. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17635994 Free PMC article.
-
Myosin motors at neuronal synapses: drivers of membrane transport and actin dynamics.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013 Apr;14(4):233-47. doi: 10.1038/nrn3445. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23481482 Review.
References
-
- Altman, D., Sweeney, H. L., and Spudich, J. A. (2004). The mechanism of myosin VI translocation and its load-induced anchoring. Cell 116, 737-749. - PubMed
-
- Awan, A., Lucic, M. R., Shaw, D. M., Sheppard, F., Westwater, C., Lyons, S. A., and Stern, P. L. (2002). 5T4 interacts with TIP-2/GIPC, a PDZ protein, with implications for metastasis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 290, 1030-1036. - PubMed
-
- Blobe, G. C., Liu, X., Fang, S. J., How, T., and Lodish, H. F. (2001). A novel mechanism for regulating transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signaling. functional modulation of type III TGF-β receptor expression through interaction with the PDZ domain protein, GIPC. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 39608-39617. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

