Effects of calcineurin activation on insulin-, AICAR- and contraction-induced glucose transport in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 15975979
- PMCID: PMC1474191
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.090829
Effects of calcineurin activation on insulin-, AICAR- and contraction-induced glucose transport in skeletal muscle
Abstract
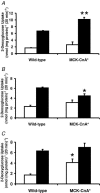
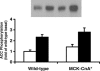
Skeletal muscle is composed of fast- and slow-twitch fibres with distinctive physiological and metabolic properties. The calmodulin-activated serine/threonine protein phosphatase calcineurin activates fast- to slow-twitch skeletal muscle remodelling through the induction of the slow-twitch skeletal muscle fibre gene expression programme, thereby enhancing insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and offering protection against dietary-induced insulin resistance. Given the profound influence of skeletal muscle fibre type on insulin-mediated responses, we determined whether the fast- to slow-twitch fibre-type transformation leads to alterations in insulin-independent glucose uptake in transgenic mice expressing a constitutively active form of calcineurin (MCK-CnA* mice). We determined whether skeletal muscle remodelling by activated calcineurin alters glucose transport in response to the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activator 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-beta-D-ribofuranoside (AICAR) or muscle contraction, two divergent insulin-independent activators of glucose transport. While insulin-stimulated glucose transport was increased 52%, the AICAR effect on glucose transport was 27% lower in MCK-CnA* mice versus wild-type mice (P < 0.05). In contrast, glucose transport was similar between genotypes after in vitro muscle contraction. Fibre-type transformation was associated with increased AMPKgamma1, decreased AMPKgamma3 and unchanged AMPKgamma2 protein expression between MCK-CnA* and wild-type mice (P < 0.05). The loss of AICAR-mediated glucose uptake is coupled to changes in the AMPK isoform expression, suggesting fibre-type dependence of the AICAR responses on glucose uptake. In conclusion, improvements in skeletal muscle glucose transport in response to calcineurin-induced muscle remodelling are limited to insulin action.
Figures



References
-
- Ai H, Ihlemann J, Hellsten Y, Lauritzen HP, Hardie DG, Galbo H, Ploug T. Effect of fiber type and nutritional state on AICAR- and contraction-stimulated glucose transport in rat muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002;282:E1291–E1300. - PubMed
-
- Barnes BR, Marklund S, Steiler TL, Walter M, Hjalm G, Amarger V, Mahlapuu M, Leng Y, Johansson C, Galuska D, Lindgren K, Abrink M, Stapleton D, Zierath JR, Andersson L. The AMPK-gamma 3 isoform has a key role for carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in glycolytic skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:38441–38447. - PubMed
-
- Barnes BR, Ryder JW, Steiler TL, Fryer LGD, Carling D, Zierath JR. Isoform-specific regulation of 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase in skeletal muscle from obese Zucker (fa/fa) rats in response to contraction. Diabetes. 2002;51:2703–2708. - PubMed
-
- Daugaard JR, Nielsen JN, Kristiansen S, Andersen JL, Hargreaves M, Richter EA. Fiber type-specific expression of GLUT4 in human skeletal muscle: influence of exercise training. Diabetes. 2000;49:1092–1095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

