Cell shrinkage as a signal to apoptosis in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts
- PMID: 15975986
- PMCID: PMC1474190
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.087130
Cell shrinkage as a signal to apoptosis in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts
Abstract
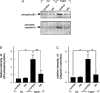
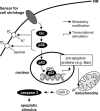
Cell shrinkage is a hallmark of the apoptotic mode of programmed cell death, but it is as yet unclear whether a reduction in cell volume is a primary activation signal of apoptosis. Here we studied the effect of an acute elevation of osmolarity (NaCl or sucrose additions, final osmolarity 687 mosmol l(-1)) on NIH 3T3 fibroblasts to identify components involved in the signal transduction from shrinkage to apoptosis. After 1.5 h the activity of caspase-3 started to increase followed after 3 h by the appearance of many apoptotic-like bodies. The caspase-3 activity increase was greatly enhanced in cells expressing a constitutively active G protein, Rac (RacV12A3 cell), indicating that Rac acts upstream to caspase-3 activation. The stress-activated protein kinase, p38, was significantly activated by phosphorylation within 30 min after induction of osmotic shrinkage, the phosphorylation being accelerated in fibroblasts overexpressing Rac. Conversely, the activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk1/2) was initially significantly decreased. Subsequent to activation of p38, p53 was activated through serine-15 phosphorylation, and active p53 was translocated from the cytosol to the nucleus. Inhibition of p38 in Rac cells reduced the activation of both p53 and caspase-3. After 60 min in hypertonic medium the rate constants for K+ and taurine efflux were increased, particular in Rac cells. We suggest the following sequence of events in the cell shrinkage-induced apoptotic response: cellular shrinkage activates Rac, with activation of p38, followed by phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of p53, resulting in permeability increases and caspase-3 activation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Opposite effects of Ha-Ras and Ki-Ras on radiation-induced apoptosis via differential activation of PI3K/Akt and Rac/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.Oncogene. 2004 Jan 8;23(1):9-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206982. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 14712206
-
Clostridium difficile toxin A-induced colonocyte apoptosis involves p53-dependent p21(WAF1/CIP1) induction via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.Gastroenterology. 2005 Dec;129(6):1875-88. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.09.011. Gastroenterology. 2005. PMID: 16344056
-
UVB-mediated activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase enhances resistance of normal human keratinocytes to apoptosis by stabilizing cytoplasmic p53.Biochem J. 2002 Jul 1;365(Pt 1):133-45. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020072. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12071847 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of DNA fragmentation: the role of caspases and phosphorylation.FEBS J. 2011 Feb;278(3):427-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07975.x. Epub 2010 Dec 23. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21182594 Review.
-
Role of ion transport in control of apoptotic cell death.Compr Physiol. 2012 Jul;2(3):2037-61. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c110046. Compr Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23723032 Review.
Cited by
-
Stress-induced modulation of volume-regulated anions channels in human alveolar carcinoma cells.Physiol Rep. 2018 Sep;6(19):e13869. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13869. Physiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30318853 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol- and/or Taurine-Induced Oxidative Stress in Chick Embryos.J Amino Acids. 2013;2013:240537. doi: 10.1155/2013/240537. Epub 2013 Mar 21. J Amino Acids. 2013. PMID: 23606945 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic, Integrated Study on the Neuroprotective Effects of Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Revealed by (1)H NMR-Based Metabonomics and the NF-κB Pathway.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:147362. doi: 10.1155/2013/147362. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23710208 Free PMC article.
-
Fate of hypertonicity-stressed corneal epithelial cells depends on differential MAPK activation and p38MAPK/Na-K-2Cl cotransporter1 interaction.Exp Eye Res. 2007 Feb;84(2):361-72. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2006.10.011. Epub 2006 Nov 30. Exp Eye Res. 2007. PMID: 17140565 Free PMC article.
-
CrossTalk proposal: Cell volume changes are an essential step in the cell death machinery.J Physiol. 2013 Dec 15;591(24):6119-21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.258632. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24339145 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Anbari K, Schultz RM. Effect of sodium and betaine in culture media on development and relative rates of protein synthesis in preimplantation mouse embryos in vitro. Mol Reprod Dev. 1993;35:24–28. - PubMed
-
- Aznar S, Fernandez-Valeron P, Espina C, Lacal JC. Rho GTPases: potential candidates for anticancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2004;206:181–191. - PubMed
-
- Bargonetti J, Manfredi JJ. Multiple roles of the tumor suppressor p53. Current Opinion Oncol. 2002;14:86–91. - PubMed
-
- Beisner KH. August Krogh Institute, University of Copenhagen; 2004. Volume regulation in NIH-3T3 fibroblasts: Effect of constitutively active RhoA, Rac1 and H-Ras. Masters Thesis.
-
- Best L, Sheader EA, Brown PD. A volume-activated anion conductance in insulin-secreting cells. Pflugers Arch. 1996;431:363–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

