The evolution of vertebrate Toll-like receptors
- PMID: 15976025
- PMCID: PMC1172252
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0502272102
The evolution of vertebrate Toll-like receptors
Abstract
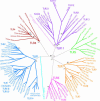
The complete sequences of Takifugu Toll-like receptor (TLR) loci and gene predictions from many draft genomes enable comprehensive molecular phylogenetic analysis. Strong selective pressure for recognition of and response to pathogen-associated molecular patterns has maintained a largely unchanging TLR recognition in all vertebrates. There are six major families of vertebrate TLRs. This repertoire is distinct from that of invertebrates. TLRs within a family recognize a general class of pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Most vertebrates have exactly one gene ortholog for each TLR family. The family including TLR1 has more species-specific adaptations than other families. A major family including TLR11 is represented in humans only by a pseudogene. Coincidental evolution plays a minor role in TLR evolution. The sequencing phase of this study produced finished genomic sequences for the 12 Takifugu rubripes TLRs. In addition, we have produced >70 gene models, including sequences from the opossum, chicken, frog, dog, sea urchin, and sea squirt.
Figures


References
-
- Aderem, A. & Ulevitch, R. J. (2000) Nature 406, 782-787. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov, R. & Janeway, C. A. (2000) Immunol. Rev. 173, 89-97. - PubMed
-
- Oshiumi, H., Tsujita, T., Shida, K., Matsumoto, M., Ikeo, K. & Seya, T. (2003) Immunogenetics 54, 791-800. - PubMed
-
- Jault, C., Pichon, L. & Chluba, J. (2004) Mol. Immunol. 40, 759-771. - PubMed
-
- Meijer, A. H., Krens, S. F. G., Rodriguez, I. A. M., He, S. N., Bitter, W., Snaar-Jagalska, B. E. & Spaink, H. P. (2004) Mol. Immunol. 40, 773-783. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

