Firing pattern and rapid modulation of activity by estrogen in primate luteinizing hormone releasing hormone-1 neurons
- PMID: 15976055
- PMCID: PMC1479770
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2005-0435
Firing pattern and rapid modulation of activity by estrogen in primate luteinizing hormone releasing hormone-1 neurons
Abstract
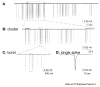
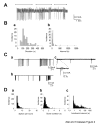
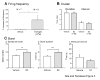
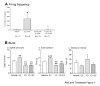
We have shown previously that cultured LHRH-1 neurons, derived from monkey olfactory placode region, exhibit pulsatile LHRH-1 release at hourly intervals and spontaneous intracellular calcium oscillations, which synchronize at a frequency similar to LHRH-1 release. Brief application of estrogen induced a rapid increase in the frequency of intracellular calcium oscillations and the frequency of synchronizations. The estrogen-induced frequency of intracellular calcium oscillations was mediated by estrogen receptors (ER), whereas the frequency of synchronizations was not mediated by ER. In the present study, we further examined the rapid action of estrogen using patch-clamp recording in primate LHRH-1 neurons. Cell-attached patch-clamp recording showed that LHRH-1 neurons exhibited monophasic or biphasic action currents that were sensitive to an increase in extracellular K+ and the sodium channel blocker tetrodotoxin. The majority (90%) of LHRH-1 neurons showed irregular firing patterns composed of bursts and irregular beatings of action currents, which further formed a "cluster" firing pattern. Brief application of 17beta-estradiol (1 nM) increased the firing frequency and burst duration of LHRH-1 neurons with a latency of 60-120 sec for up to 25 min. ICI182,780, an ER antagonist, blocked the 17beta-estradiol-induced increase in the firing activity of LHRH-1 neurons. These results suggest that 1) primate LHRH-1 neurons exhibit complex firing patterns composed of activities with different time domains, 2) estrogen causes rapid stimulatory action of firing activity, and 3) this estrogen action is mediated by ER in primate LHRH-1 neurons.
Figures



References
-
- Wilson RC, Kesner JS, Kaufman JM, Uemura T, Akema T, Knobil E. Central electrophysiologic correlates of pulsatile luteinizing hormone secretion in the rhesus monkey. Neuroendocrinology. 1984;39:256–260. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka T, Ozawa T, Hoshino K, Mori Y. Changes in the gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse generator activity during the estrous cycle in the goat. Neuroendocrinology. 1995;62:553–561. - PubMed
-
- Nishihara M, Takeuchi Y, Tanaka T, Mori Y. Electrophysiological correlates of pulsatile and surge gonadotrophin secretion. Rev Reprod. 1999;4:110–116. - PubMed
-
- Terasawa E 2003 Pulse generation in LHRH neurons. In: Handa R, Hayashi S, Terasawa E, Kawata M (eds) Neuroplasticity, Development, and Steroid Hormone Action. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 153–168
-
- Terasawa E. Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) neurons: Mechanism of pulsatile LHRH release. Vitam Horm. 2001;63:91–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

