Standardization of cytokine flow cytometry assays
- PMID: 15978127
- PMCID: PMC1184077
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-6-13
Standardization of cytokine flow cytometry assays
Abstract
Background: Cytokine flow cytometry (CFC) or intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) can quantitate antigen-specific T cell responses in settings such as experimental vaccination. Standardization of ICS among laboratories performing vaccine studies would provide a common platform by which to compare the immunogenicity of different vaccine candidates across multiple international organizations conducting clinical trials. As such, a study was carried out among several laboratories involved in HIV clinical trials, to define the inter-lab precision of ICS using various sample types, and using a common protocol for each experiment (see additional files online).
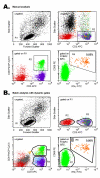
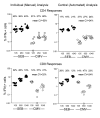
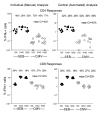
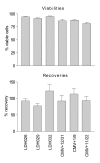
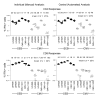
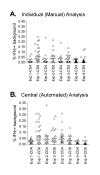
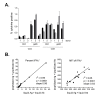
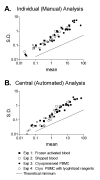
Results: Three sample types (activated, fixed, and frozen whole blood; fresh whole blood; and cryopreserved PBMC) were shipped to various sites, where ICS assays using cytomegalovirus (CMV) pp65 peptide mix or control antigens were performed in parallel in 96-well plates. For one experiment, antigens and antibody cocktails were lyophilised into 96-well plates to simplify and standardize the assay setup. Results ((CD4+)cytokine+ cells and (CD8+)cytokine+ cells) were determined by each site. Raw data were also sent to a central site for batch analysis with a dynamic gating template. Mean inter-laboratory coefficient of variation (C.V.) ranged from 17-44% depending upon the sample type and analysis method. Cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) yielded lower inter-lab C.V.'s than whole blood. Centralized analysis (using a dynamic gating template) reduced the inter-lab C.V. by 5-20%, depending upon the experiment. The inter-lab C.V. was lowest (18-24%) for samples with a mean of > 0.5% IFNgamma + T cells, and highest (57-82%) for samples with a mean of < 0.1% IFNgamma + cells.
Conclusion: ICS assays can be performed by multiple laboratories using a common protocol with good inter-laboratory precision, which improves as the frequency of responding cells increases. Cryopreserved PBMC may yield slightly more consistent results than shipped whole blood. Analysis, particularly gating, is a significant source of variability, and can be reduced by centralized analysis and/or use of a standardized dynamic gating template. Use of pre-aliquoted lyophilized reagents for stimulation and staining can provide further standardization to these assays.
Figures


References
-
- Maecker HT. Cytokine flow cytometry. In: Hawley TS, Hawley RG, editor. Flow Cytometry Protocols. 2nd. Totowa, NJ , Humana Press; 2004. pp. 95–107. (Meth Molec Biol). Walker J.
-
- Cox JH, Ferrari G, Kalams SA, Lopaczynski W, Oden N, Group ELISPOTS. Results of an ELISPOT proficiency panel conducted in 11 laboratories participating in international human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vaccine trials. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2005. - PubMed
-
- McMichael AJ, Hanke T. HIV vaccines 1983-2003. Nat Med. 2003;9:874–880. - PubMed
-
- Pantaleo G, Koup RA. Correlates of immune protection in HIV-1 infection: what we know, what we don't know, what we should know. Nat Med. 2004;10:806–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

