Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: pattern of expression and correlation with clinical outcome
- PMID: 15978137
- PMCID: PMC1188078
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-3-26
Expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: pattern of expression and correlation with clinical outcome
Abstract
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is a tumor derived from epithelial cells and Epstein-Barr virus infection has been reported to be a cause of this disease. Chemokine receptor CXCR4 was found to be involved in HIV infection and was highly expressed in human malignant breast tumors and the ligand for CXCR4, CXCL12 (SDF-1), exhibited high expression in organs in which breast cancer metastases are often found. The metastatic pattern of NPC is quite similar to that of malignant breast tumors. In this study, we investigated the expression of CXCR4 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) tissues by immunohistostaining. We found different staining patterns, which included localization in the nucleus, membrane, cytoplasm or a combination of them. The staining intensity was also variable among samples. The metastatic rates in patients with high compared to low or absent expression was 38.6% versus 19.8%, respectively (P = 0.004). High expression of CXCR4 was associated with poor overall survival (OS = 67.05% versus 82.08%, P = 0.0225). These results suggest that CXCR4 may be involved in the progression of NPC and that a high level of CXCR4 expression could be used as a prognostic factor.
Figures
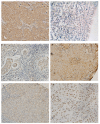
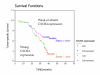
References
-
- Hu LF, Chen F, Zheng X, Ernberg I, Cao SL, Christensson B, Klein G, Winberg G. Clonability and tumorigenicity of human epithelial cells expressing the EBV encoded membrane protein LMP1. Oncogene. 1993;8:1575–1583. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

