Early detection of dominant Env-specific and subdominant Gag-specific CD8+ lymphocytes in equine infectious anemia virus-infected horses using major histocompatibility complex class I/peptide tetrameric complexes
- PMID: 15979679
- PMCID: PMC3342685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.05.025
Early detection of dominant Env-specific and subdominant Gag-specific CD8+ lymphocytes in equine infectious anemia virus-infected horses using major histocompatibility complex class I/peptide tetrameric complexes
Abstract
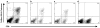
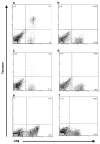
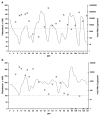
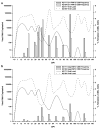
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) are critical for control of lentiviruses, including equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV). Measurement of equine CTL responses has relied on chromium-release assays, which do not allow accurate quantitation. Recently, the equine MHC class I molecule 7-6, associated with the ELA-A1 haplotype, was shown to present both the Gag-GW12 and Env-RW12 EIAV CTL epitopes. In this study, 7-6/Gag-GW12 and 7-6/Env-RW12 MHC class I/peptide tetrameric complexes were constructed and used to analyze Gag-GW12- and Env-RW12-specific CTL responses in two EIAV-infected horses (A2164 and A2171). Gag-GW12 and Env-RW12 tetramer-positive CD8+ cells were identified in nonstimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells as early as 14 days post-EIAV inoculation, and frequencies of tetramer-positive cells ranged from 0.4% to 6.7% of nonstimulated peripheral blood CD8+ cells during the 127-day study period. Although both horses terminated the initial viremic peak, only horse A2171 effectively controlled viral load. Neutralizing antibody was present during the initial control of viral load in both horses, but the ability to maintain control correlated with Gag-GW12-specific CD8+ cells in A2171. Despite Env-RW12 dominance, Env-RW12 escape viral variants were identified in both horses and there was no correlation between Env-RW12-specific CD8+ cells and control of viral load. Although Gag-GW12 CTL escape did not occur, a Gag-GW12 epitope variant arose in A2164 that was recognized less efficiently than the original epitope. These data indicate that tetramers are useful for identification and quantitation of CTL responses in horses, and suggest that the observed control of EIAV replication and clinical disease was associated with sustained CTL recognition of Gag-specific epitopes.
Figures

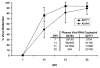

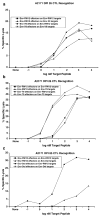
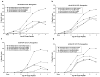

References
-
- Altman JD, Moss PA, Goulder PJ, Barouch DH, McHeyzer-Williams MG, Bell JI, McMichael AJ, Davis MM. Phenotypic analysis of antigen-specific T lymphocytes. Science. 1996;274:94–96. - PubMed
-
- Bailey E. Identification and genetics of horse lymphocyte alloantigens. Immunogenetics. 1980;11:499–506. - PubMed
-
- Betts MR, Krowka JF, Kepler TB, Davidian M, Christopherson C, Kwok S, Louie L, Eron J, Sheppard H, Frelinger JA. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity is inversely correlated with HIV type 1 viral load in HIV type 1-infected long-term survivors. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1999;15:1219–1228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

