Differences in cell death induction by Phytophthora Elicitins are determined by signal components downstream of MAP kinase kinase in different species of Nicotiana and cultivars of Brassica rapa and Raphanus sativus
- PMID: 15980203
- PMCID: PMC1176420
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.058388
Differences in cell death induction by Phytophthora Elicitins are determined by signal components downstream of MAP kinase kinase in different species of Nicotiana and cultivars of Brassica rapa and Raphanus sativus
Abstract
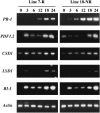
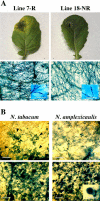
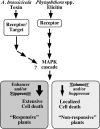
Elicitins are small, secreted proteins produced by species of the plant-pathogenic oomycete Phytophthora. They induce hypersensitive cell death in most Nicotiana species and in some cultivars of Brassica rapa and Raphanus sativus. In this study, two true-breeding Fast Cycling B. rapa lines were established that showed severe necrosis (line 7-R) or no visible response (line 18-NR) after treatment with elicitin. Unexpectedly, microscopic examination revealed localized cell death in line 18-NR plants, and expression levels of various defense-marker genes were comparable in both lines. These results suggested that both "responsive" and "nonresponsive" plants responded to elicitin but differed in the extent of the cell death response. Expression of a constitutively active form of Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) MAP kinase kinase 4 (AtMEK4(DD)) also induced rapid development of confluent cell death in line 7-R, whereas line 18-NR showed no visible cell death. Similarly, elicitin-responsive Nicotiana species and R. sativus cultivars showed significantly stronger cell death responses following expression of AtMEK4(DD) compared with nonresponsive species/cultivars. Line 7-R also showed higher sensitivity to toxin-containing culture filtrates produced by Alternaria brassicicola, and toxin sensitivity cosegregated with elicitin responsiveness, suggesting that the downstream responses induced by elicitin and Alternaria toxin share factors that control the extent of cell death. Interestingly, elicitin responsiveness was shown to correlate with greater susceptibility to A. brassicicola (a necrotroph) in B. rapa but less susceptibility to Phytophthora nicotianae (a hemibiotroph) in Nicotiana, suggesting a more extensive cell death response could cause opposite effects on the outcomes of biotrophic versus necrotrophic plant-pathogen interactions.
Figures




References
-
- Asai T, Tena G, Plotnikova J, Willmann MR, Chiu W-L, Gomez-Gomez L, Boller T, Ausubel FM, Sheen J (2002) MAP kinase signalling cascade in Arabidopsis innate immunity. Nature 415: 977–983 - PubMed
-
- Blein J-P, Coutos-Thevenot P, Marion D, Ponchet M (2002) From elicitins to lipid-transfer proteins: a new insight in cell signalling involved in plant defence mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci 7: 293–296 - PubMed
-
- Boissy G, de La Fortelle E, Kahn R, Huet J-C, Bricogne G, Pernollet J-C, Brunie S (1996) Crystal structure of a fungal elicitor secreted by Phytophthora cryptogea, a member of a novel class of plant necrotic proteins. Structure 4: 1429–1439 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

