Leukocyte diapedesis in vivo induces transient loss of tight junction protein at the blood-retina barrier
- PMID: 15980240
- PMCID: PMC2478725
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.04-1333
Leukocyte diapedesis in vivo induces transient loss of tight junction protein at the blood-retina barrier
Abstract
Purpose: Although much is now understood about the molecular structure of tight junctions (TJs), little is known about the regulation of their function during neural inflammatory disease processes in vivo. The mechanisms by which leukocytes transmigrate the blood-retina barrier (BRB) without affecting endothelial permeability are controversial.
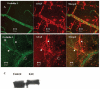
Methods: Confocal immunofluorescence microscopy of ex vivo retinal wholemounts was used to study BRB integrity during leukocyte adhesion and migration during experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU). Western blot analysis was used to measure levels of TJ proteins in EAU retina and RPE and in normal retina or RPE cultured with cytokines or chemokines.
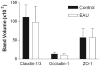
Results: No evidence for discontinuity or other weakness of the endothelial or epithelial barrier at tricellular corners was observed, and maximum disruption of TJ protein expression was focused in retinal venules correlating with sites of leukocyte extravasation. Areas of maximum TJ protein loss in vivo also correlated with redistribution or loss of ensheathing astrocyte processes on venules but not adjacent capillaries or arterioles. Exposure of normal choroidal and retinal explants ex vivo to cytokines and chemokines alone did not downregulate total occludin-1 or claudin-3 TJ protein expression.
Conclusions: The data presented herein support an active role for leukocytes in TJ disruption and blood-retina barrier (BRB) breakdown during retinal inflammation and further implicate venule microenvironment as a key factor in leukocyte recruitment to retinal tissue in vivo.
Figures






References
-
- Xu H, Manivannan A, Liversidge J, Sharp PF, Forrester JV, Crane IJ. Requirements for passage of T lymphocytes across non-inflamed retinal microvessels. J Neuroimmunol. 2003;142:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Xu H, Forrester JV, Liversidge J, Crane IJ. Leukocyte trafficking in experimental autoimmune uveitis: breakdown of blood-retinal barrier and upregulation of cellular adhesion molecules. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:226–234. - PubMed
-
- Wolburg H, Lippoldt A. Tight junctions of the blood-brain barrier: development, composition and regulation. Vasc Pharmacol. 2002;38:323–337. - PubMed
-
- Barber AJ, Antonetti DA, Gardner TW, the Penn State Retina Research Group Altered expression of retinal occludin and glial fibrillary acidic protein in experimental diabetes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:3561–3568. - PubMed
-
- Morcos Y, Hosie MJ, Bauer HC, Chan-Ling T. Immunolocalization of occludin and claudin-1 to tight junctions in intact CNS vessels of mammalian retina. J Neurocytol. 2001;30:107–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

