Reduced susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus to vancomycin and platelet microbicidal protein correlates with defective autolysis and loss of accessory gene regulator (agr) function
- PMID: 15980337
- PMCID: PMC1168700
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.7.2687-2692.2005
Reduced susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus to vancomycin and platelet microbicidal protein correlates with defective autolysis and loss of accessory gene regulator (agr) function
Abstract
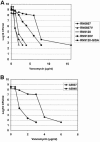
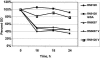
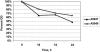
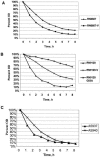
Loss of agr function, vancomycin exposure, and abnormal autolysis have been linked with both development of the GISA phenotype and low-level resistance in vitro to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal proteins (tPMPs). We examined the potential in vitro interrelationships among these parameters in well-characterized, isogenic laboratory-derived and clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates. The laboratory-derived S. aureus strains included RN6607 (agrII-positive parent) and RN6607V (vancomycin-passaged variant; hetero-GISA), RN9120 (RN6607 agr::tetM; agr II knockout parent), RN9120V (vancomycin-passaged variant), and RN9120-GISA (vancomycin passaged, GISA). Two serial isolates from a vancomycin-treated patient with recalcitrant, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) endocarditis were also studied: A5937 (agrII-positive initial isolate) and A5940 (agrII-defective/hetero-GISA isolate obtained after prolonged vancomycin administration). In vitro tPMP susceptibility phenotypes were assessed after exposure of strains to either 1 or 2 mug/ml. Triton X-100- and vancomycin-induced lysis profiles were determined spectrophotometrically. For agrII-intact strain RN6607, vancomycin exposure in vitro was associated with modest increases in vancomycin MICs and reduced killing by tPMP, but no change in lysis profiles. In contrast, vancomycin exposure of agrII-negative RN9120 yielded a hetero-GISA phenotype and was associated with defects in lysis and reduced in vitro killing by tPMP. In the clinical isolates, loss of agrII function during prolonged vancomycin therapy was accompanied by emergence of the hetero-GISA phenotype and reduced tPMP killing, with no significant change in lysis profiles. An association was identified between loss of agrII function and the emergence of hetero-GISA phenotype during either in vitro or in vivo vancomycin exposure. In vitro, these events were associated with defective lysis and reduced susceptibility to tPMP. The precise mechanism(s) underlying these findings is the subject of current investigations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accessory gene regulator (agr) locus in geographically diverse Staphylococcus aureus isolates with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 May;46(5):1492-502. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.5.1492-1502.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 11959587 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of prolonged vancomycin administration on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a patient with recurrent bacteraemia.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006 Apr;57(4):699-704. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl030. Epub 2006 Feb 7. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16464892
-
Correlation of vancomycin and daptomycin susceptibility in Staphylococcus aureus in reference to accessory gene regulator (agr) polymorphism and function.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007 Jun;59(6):1190-3. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm091. Epub 2007 Apr 13. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17434881
-
Adaptation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the face of vancomycin therapy.Clin Infect Dis. 2006 Jan 1;42 Suppl 1:S40-50. doi: 10.1086/491713. Clin Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 16323119 Review.
-
Reduced glycopeptide susceptibility in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007 Nov;30(5):398-408. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.07.011. Epub 2007 Sep 20. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2007. PMID: 17888634 Review.
Cited by
-
Vancomycin tolerance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: influence of vancomycin, daptomycin, and telavancin on differential resistance gene expression.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Aug;56(8):4422-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00676-12. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22687502 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated in Poland in 1996 to 2004 that were deficient in species-specific proteins.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Nov;44(11):4018-24. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01164-06. Epub 2006 Sep 27. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17005746 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of endocarditis caused by methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus developing nonsusceptibility to daptomycin.J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Jan;46(1):220-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00660-07. Epub 2007 Nov 14. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18003803 Free PMC article.
-
Species-Wide Phylogenomics of the Staphylococcus aureus Agr Operon Revealed Convergent Evolution of Frameshift Mutations.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0133421. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01334-21. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35044202 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-like Fragments Inhibit agr-Mediated Virulence Expression in Staphylococcus aureus.Sci Rep. 2019 May 1;9(1):6786. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42853-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31043623 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bayer, A. S., R. Prasad, J. Chandra, A. Koul, M. Smriti, A. Varma, R. A. Skurray, N. Firth, M. H. Brown, S. P. Koo, and M. R. Yeaman. 2000. In vitro resistance of Staphylococcus aureus to thrombin-induced platelets microbicidal protein is associated with alterations in cytoplasmic membrane fluidity. Infect. Immun. 68:3548-3553. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bayer, A. S., D. Cheng, M. R. Yeaman, G. Ralph Corey, R. S. McClelland, L. J. Harrel, and V. G. Fowler. 1998. In vitro resistance to thrombin-induced platelet microbicidal protein among clinical bacteremic isolates of Staphylococcus aureus correlates with an endovascular infectious source. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42:3169-3172. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyle-Vavra, S., R. B. Carey, and R. S. Daum. 2001. Development of vancomycin and lysostaphin resistance in a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolate. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 48:617-625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

