Efficacy of nebulized liposomal amphotericin B in treatment of experimental pulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 15980392
- PMCID: PMC1168712
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.7.3028-3030.2005
Efficacy of nebulized liposomal amphotericin B in treatment of experimental pulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
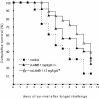
The efficacy of therapeutic aerosolized amphotericin B (AMB) was studied in a steroid-immunosuppressed murine model of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Nebulized liposomal AMB can be a valid approach to the treatment of this infection, with subjects showing significantly improved survival relative to that of subjects given intravenous deoxycholate AMB, as well as lower lung weights and pulmonary glucosamine levels.
Figures

References
-
- Allen, S. D., K. N. Sorensen, M. J. Nejdl, C. Durrant, and R. T. Proffit. 1994. Prophylactic efficacy of aerosolized liposomal (AmBisome) and non-liposomal (Fungizone) amphotericin B in murine pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 34:1001-1013. - PubMed
-
- Becker, M. J., S. de Marie, M. H. Fens, W. C. Hop, H. A. Verbrugh, and I. A. Bakker-Woudenberg. 2002. Enhanced antifungal efficacy in experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis by combination of AmBisome with Fungizone as assessed by several parameters of antifungal response. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 49:813-820. - PubMed
-
- Denning, D. W. 1998. Invasive aspergillosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 26:781-805. - PubMed
-
- Denning, D. W., C. C. Kibler, and R. A. Barnes on behalf of the British Society for Medical Mycology. 2003. British Society for Medical Mycology proposed standards of care for patients with invasive fungal infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 3:230-240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

