Heterogeneity of genotype-phenotype correlation among macrolide-resistant Streptococcus agalactiae isolates
- PMID: 15980405
- PMCID: PMC1168644
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.7.3080-3082.2005
Heterogeneity of genotype-phenotype correlation among macrolide-resistant Streptococcus agalactiae isolates
Abstract
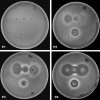
Seventy-four erythromycin-resistant group B Streptococcus isolates were analyzed regarding their phenotype-genotype and phenotype-serotype correlation. Four different phenotypes were assessed, one of them for the first time. ermB and ermTR were the most frequent genotypes (80%). The most prevalent serotype III showed great phenotypic variability while serotype V was strongly associated only with two different phenotypes.
Figures
References
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious Disease and Committee on Fetus and Newborn. 1997. Revised guidelines for prevention of early-onset group B streptococcal (GBS) infection. Pediatrics 99:489-496. - PubMed
-
- Berner, R., A. Bender, C. Rensing, J. Forster, and M. Brandis. 1999. Low prevalence of the immunoglobulin-A-binding β antigen of the C protein among Streptococcus agalactiae isolates causing neonatal sepsis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 18:545-550. - PubMed
-
- Berner, R., R. F. Schumacher, S. Bartelt, J. Forster, and M. Brandis. 1998. Bacteremia in hospitalized children: predisposing conditions and case-related microorganisms. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 17:337-340. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1996. Prevention of perinatal group B streptococcal disease: a public health perspective. Morbid. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 45:1-24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

