Cooperative uptake of microcin E492 by receptors FepA, Fiu, and Cir and inhibition by the siderophore enterochelin and its dimeric and trimeric hydrolysis products
- PMID: 15980406
- PMCID: PMC1168642
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.49.7.3083-3086.2005
Cooperative uptake of microcin E492 by receptors FepA, Fiu, and Cir and inhibition by the siderophore enterochelin and its dimeric and trimeric hydrolysis products
Abstract
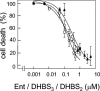
Microcin E492 uptake by FepA, Fiu, and Cir is cooperative, with FepA being the main receptor. No TonB-mediated interaction with the ferric catecholate receptors is needed for microcin to exert action at the cytoplasmic membrane. Microcin E492 uptake by the receptors is inhibited by the dimer and trimer of dihydroxybenzoylserine.
Figures

References
-
- Braun, V., S. I. Patzer, and K. Hantke. 2002. Ton-dependent colicins and microcins: modular design and evolution. Biochimie 84:365-380. - PubMed
-
- Bray, D., and T. Duke. 2004. Conformational spread: the propagation of allosteric stages in large multiprotein complexes. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. 33:53-73. - PubMed
-
- Corsini, G., M. Baeza, O. Monasterio, and R. Lagos. 2002. The expression of genes involved in microcin maturation regulates the production of active microcin E492. Biochimie 84:539-544. - PubMed
-
- de Lorenzo, V. 1984. Isolation and characterization of microcin E492 from Klebsiella pneumoniae. Arch. Microbiol. 139:72-75. - PubMed
-
- Destoumieux-Garzon, D., X. Thomas, M. Santamaria, C. Goulard, M. Barthélémy, B. Boscher, Y. Bassin, G. Molle, A.-M. Pons, L. Letellier, J. Peduzzi, and S. Rebuffat. 2003. Microcin E492 antibacterial activity: evidence for a TonB-dependent inner membrane permeabilization on Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 49:1031-1041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

