FOOTER: a web tool for finding mammalian DNA regulatory regions using phylogenetic footprinting
- PMID: 15980508
- PMCID: PMC1160181
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki420
FOOTER: a web tool for finding mammalian DNA regulatory regions using phylogenetic footprinting
Abstract
FOOTER is a newly developed algorithm that analyzes homologous mammalian promoter sequences in order to identify transcriptional DNA regulatory 'signals'. FOOTER uses prior knowledge about the binding site preferences of the transcription factors (TFs) in the form of position-specific scoring matrices (PSSMs). The PSSM models are generated from known mammalian binding sites from the TRANSFAC database. In a test set of 72 confirmed binding sites (most of them not present in TRANSFAC) of 19 TFs, it exhibited 83% sensitivity and 72% specificity. FOOTER is accessible over the web at http://biodev.hgen.pitt.edu/Footer/.
Figures
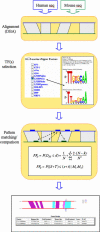
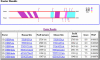
References
-
- Hughes J.D., Estep P.W., Tavazoie S., Church G.M. Computational identification of cis-regulatory elements associated with groups of functionally related genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Mol. Biol. 2000;296:1205–1214. - PubMed
-
- Workman C.T., Stormo G.D. ANN-Spec: a method for discovering transcription factor binding sites with improved specificity. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2000:467–478. - PubMed
-
- Hertz G.Z., Hartzell G.W., III, Stormo G.D. Identification of consensus patterns in unaligned DNA sequences known to be functionally related. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1990;6:81–92. - PubMed
-
- GuhaThakurta D., Stormo G.D. Identifying target sites for cooperatively binding factors. Bioinformatics. 2001;17:608–621. - PubMed
-
- Bailey T.L., Elkan C. The value of prior knowledge in discovering motifs with MEME. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1995;3:21–29. - PubMed

