nsSNPAnalyzer: identifying disease-associated nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms
- PMID: 15980516
- PMCID: PMC1160133
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki372
nsSNPAnalyzer: identifying disease-associated nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms
Abstract
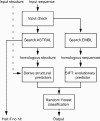
Nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms (nsSNPs) are prevalent in genomes and are closely associated with inherited diseases. To facilitate identifying disease-associated nsSNPs from a large number of neutral nsSNPs, it is important to develop computational tools to predict the nsSNP's phenotypic effect (disease-associated versus neutral). nsSNPAnalyzer, a web-based software developed for this purpose, extracts structural and evolutionary information from a query nsSNP and uses a machine learning method called Random Forest to predict the nsSNP's phenotypic effect. nsSNPAnalyzer server is available at http://snpanalyzer.utmem.edu/.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prediction of the phenotypic effects of non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms using structural and evolutionary information.Bioinformatics. 2005 May 15;21(10):2185-90. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti365. Epub 2005 Mar 3. Bioinformatics. 2005. PMID: 15746281
-
Structure SNP (StSNP): a web server for mapping and modeling nsSNPs on protein structures with linkage to metabolic pathways.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W384-92. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm232. Epub 2007 May 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17537826 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of deleterious nonsynonymous single-nucleotide polymorphism for human diseases.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013;2013:675851. doi: 10.1155/2013/675851. Epub 2013 Jan 30. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 23431257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Statistical geometry based prediction of nonsynonymous SNP functional effects using random forest and neuro-fuzzy classifiers.Proteins. 2008 Jun;71(4):1930-9. doi: 10.1002/prot.21838. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 18186470
-
Applications of computational algorithm tools to identify functional SNPs.Funct Integr Genomics. 2008 Nov;8(4):309-16. doi: 10.1007/s10142-008-0086-7. Epub 2008 Jun 19. Funct Integr Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18563462 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel homozygous p.Arg527Leu LMNA mutation in two unrelated Egyptian families causes overlapping mandibuloacral dysplasia and progeria syndrome.Eur J Hum Genet. 2012 Nov;20(11):1134-40. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.77. Epub 2012 May 2. Eur J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22549407 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of destabilizing SNPs in SARS-CoV2-ACE2 protein and spike glycoprotein: implications for virus entry mechanisms.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Feb;40(3):1205-1215. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1823885. Epub 2020 Sep 23. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 32964802 Free PMC article.
-
FunSAV: predicting the functional effect of single amino acid variants using a two-stage random forest model.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43847. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043847. Epub 2012 Aug 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22937107 Free PMC article.
-
SNP@Domain: a web resource of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within protein domain structures and sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 Jul 1;34(Web Server issue):W642-4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl323. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16845090 Free PMC article.
-
Innovative in Silico Approaches for Characterization of Genes and Proteins.Front Genet. 2022 May 18;13:865182. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.865182. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35664302 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stenson P.D., Ball E.V., Mort M., Phillips A.D., Shiel J.A, Thomas N.S., Abeysinghe S., Krawczak M., Cooper D.N. Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD): 2003 update. Hum. Mutat. 2003;21:577–581. - PubMed
-
- Irizarry K., Kustanovich V., Li C., Brown N., Nelson S., Wong W., Lee C.J. Comprehensive EST analysis of single nucleotide polymorphism across coding regions of the human genome. Nature Genet. 2000;26:233–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

