PriFi: using a multiple alignment of related sequences to find primers for amplification of homologs
- PMID: 15980525
- PMCID: PMC1160186
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki425
PriFi: using a multiple alignment of related sequences to find primers for amplification of homologs
Abstract
Using a comparative approach, the web program PriFi (http://cgi-www.daimi.au.dk/cgi-chili/PriFi/main) designs pairs of primers useful for PCR amplification of genomic DNA in species where prior sequence information is not available. The program works with an alignment of DNA sequences from phylogenetically related species and outputs a list of possibly degenerate primer pairs fulfilling a number of criteria, such that the primers have a maximal probability of amplifying orthologous sequences in other phylogenetically related species. Operating on a genome-wide scale, PriFi automates the first steps of a procedure for developing general markers serving as common anchor loci across species. To accommodate users with special preferences, configuration settings and criteria can be customized.
Figures
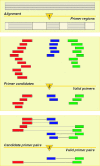


References
-
- Burpo F.J. A critical review of PCR primer design algorithms and cross-hybridization case study. 2001 Biochemistry 218 at Stanford University. Available at http://cmgm.stanford.edu/biochem218/Projects%202001/Burpo.pdf.
-
- Pertea G., Huang X., Liang F., Antonescu V., Sultana R., Karamycheva S., Lee Y., White J., Cheung F., Parvizi B., et al. TIGR Gene Indices clustering tools (TGICL): a software system for fast clustering of large EST datasets. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:651–652. - PubMed

