A robust bulk-solvent correction and anisotropic scaling procedure
- PMID: 15983406
- PMCID: PMC2808320
- DOI: 10.1107/S0907444905007894
A robust bulk-solvent correction and anisotropic scaling procedure
Abstract
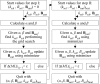
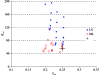
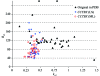
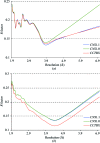
A reliable method for the determination of bulk-solvent model parameters and an overall anisotropic scale factor is of increasing importance as structure determination becomes more automated. Current protocols require the manual inspection of refinement results in order to detect errors in the calculation of these parameters. Here, a robust method for determining bulk-solvent and anisotropic scaling parameters in macromolecular refinement is described. The implementation of a maximum-likelihood target function for determining the same parameters is also discussed. The formulas and corresponding derivatives of the likelihood function with respect to the solvent parameters and the components of anisotropic scale matrix are presented. These algorithms are implemented in the CCTBX bulk-solvent correction and scaling module.
Figures

References
-
- Badger, J. (1997). Methods Enzymol.277, 344–352. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, F. C., Koetzle, T. F., Williams, G. J., Meyer, E. F. Jr, Brice, M. D., Rodgers, J. R., Kennard, O., Shimanouchi, T. & Tasumi, M. (1977). J. Mol. Biol.112, 535–542. - PubMed
-
- Blanc, E., Roversi, P., Vonrhein, C., Flensburg, C., Lea, S. M. & Bricogne, G. (2004). Acta Cryst. D60, 2210–2221. - PubMed
-
- Bricogne, G. (1991). Acta Cryst. A47, 803–829.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

