Brain activation in offspring of AD cases corresponds to 10q linkage
- PMID: 15984011
- PMCID: PMC2672820
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.20515
Brain activation in offspring of AD cases corresponds to 10q linkage
Abstract
Previously, we reported evidence of genetic heterogeneity in late-onset familial Alzheimer's disease, based on sex of affected parent, demonstrating linkage to chromosome 10q, a region identified by other groups and implicated as a quantitative trait loci for Abeta levels, in families with an affected mother. Using functional magnetic resonance imaging and a memory encoding task, we now show differential brain activation patterns among asymptomatic offspring which correspond to the previous linkage finding. These results suggest the possibility that activation patterns may prove useful as a preclinical quantitative trait related to the putative familial late-onset AD gene in this chromosome 10 region.
Figures
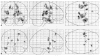
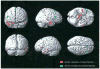
References
-
- Myers A, Wavrant De-Vrieze F, Holmans P, et al. Full genome screen for Alzheimer disease: stage II analysis. Am J Med Genet. 2002;114:235–244. - PubMed
-
- Kehoe P, Wavrant-De Vrieze F, Crook R, et al. A full genome scan for late onset Alzheimer’s disease. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:237–245. - PubMed
-
- Pericak-Vance MA, Bass MP, Yamaoka LH, et al. Complete genomic screen in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Evidence for a new locus on chromosome 12. JAMA. 1997;278:1237–1241. - PubMed
-
- Pericak-Vance MA, Bass ML, Yamaoka LH, et al. Complete genomic screen in late-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1998;19:S39–S42. - PubMed
-
- Blacker D, Bertram L, Saunders AJ, et al. Results of a high-resolution genome screen of 437 Alzheimer’s disease families. Hum Mol Genet. 2003;12:23–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

