Reliability of computerized image analysis for the evaluation of serial synovial biopsies in randomized controlled trials in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 15987488
- PMCID: PMC1175038
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1757
Reliability of computerized image analysis for the evaluation of serial synovial biopsies in randomized controlled trials in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
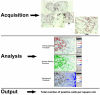
Analysis of biomarkers in synovial tissue is increasingly used in the evaluation of new targeted therapies for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This study determined the intrarater and inter-rater reliability of digital image analysis (DIA) of synovial biopsies from RA patients participating in clinical trials. Arthroscopic synovial biopsies were obtained before and after treatment from 19 RA patients participating in a randomized controlled trial with prednisolone. Immunohistochemistry was used to detect CD3+ T cells, CD38+ plasma cells and CD68+ macrophages. The mean change in positive cells per square millimetre for each marker was determined by different operators and at different times using DIA. Nonparametric tests were used to determine differences between observers and assessments, and to determine changes after treatment. The intraclass correlations (ICCs) were calculated to determine the intrarater and inter-rater reliability. Intrarater ICCs showed good reliability for measuring changes in T lymphocytes (R = 0.87), plasma cells (R = 0.62) and macrophages (R = 0.73). Analysis by Bland-Altman plots showed no systemic differences between measurements. The smallest detectable changes were calculated and their discriminatory power revealed good response in the prednisolone group compared with the placebo group. Similarly, inter-rater ICCs also revealed good reliability for measuring T lymphocytes (R = 0.68), plasma cells (R = 0.69) and macrophages (R = 0.72). All measurements identified the same cell types as changing significantly in the treated patients compared with the placebo group. The measurement of change in total positive cell numbers in synovial tissue can be determined reproducibly for various cell types by DIA in RA clinical trials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of oral prednisolone on biomarkers in synovial tissue and clinical improvement in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Dec;50(12):3783-91. doi: 10.1002/art.20664. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 15593225 Clinical Trial.
-
Synovial tissue sublining CD68 expression is a biomarker of therapeutic response in rheumatoid arthritis clinical trials: consistency across centers.J Rheumatol. 2009 Aug;36(8):1800-2. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.090348. J Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19671815
-
A randomized controlled trial with an anti-CCL2 (anti-monocyte chemotactic protein 1) monoclonal antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Aug;54(8):2387-92. doi: 10.1002/art.21975. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16869001 Clinical Trial.
-
Analyzing synovial tissue samples. What can we learn about early rheumatoid arthritis, the heterogeneity of the disease, and the effects of treatment?J Rheumatol Suppl. 2005 Jan;72:25-6. J Rheumatol Suppl. 2005. PMID: 15660460 Review.
-
Novel approaches for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: lessons from the evaluation of synovial biomarkers in clinical trials.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008 Apr;22(2):311-23. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2008.02.002. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18455687 Review.
Cited by
-
Prostaglandin E2 synthesizing enzymes in rheumatoid arthritis B cells and the effects of B cell depleting therapy on enzyme expression.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 27;6(1):e16378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016378. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21298002 Free PMC article.
-
TWEAK and its receptor Fn14 in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared to psoriatic arthritis and its response to tumour necrosis factor blockade.Ann Rheum Dis. 2010 Jan;69(1):301-4. doi: 10.1136/ard.2008.090548. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. PMID: 19147618 Free PMC article.
-
The prolactin receptor is expressed in rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis synovial tissue and contributes to macrophage activation.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016 Dec;55(12):2248-2259. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew316. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016. PMID: 27616146 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of rituximab treatment on T and B cell subsets in lymph node biopsies of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019 Jun 1;58(6):1075-1085. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key428. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019. PMID: 30649469 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling in the synovium identifies a predictive signature of absence of response to adalimumab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(2):R57. doi: 10.1186/ar2678. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19389237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tak PP. Lessons learnt from the synovial tissue response to anti-rheumatic treatment. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2000;39:817–820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

