Catabolic stress induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha in articular chondrocytes: involvement of HIF-1 alpha in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis
- PMID: 15987493
- PMCID: PMC1175045
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1765
Catabolic stress induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha in articular chondrocytes: involvement of HIF-1 alpha in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis
Erratum in
- Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(5):225
Abstract
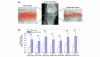
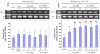
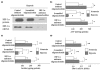
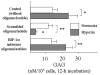
Transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 protein accumulates and activates the transcription of genes that are of fundamental importance for oxygen homeostasis - including genes involved in energy metabolism, angiogenesis, vasomotor control, apoptosis, proliferation, and matrix production - under hypoxic conditions. We speculated that HIF-1alpha may have an important role in chondrocyte viability as a cell survival factor during the progression of osteoarthritis (OA). The expression of HIF-1alpha mRNA in human OA cartilage samples was analyzed by real-time PCR. We analyzed whether or not the catabolic factors IL-1beta and H2O2 induce the expression of HIF-1alpha in OA chondrocytes under normoxic and hypoxic conditions (O2 <6%). We investigated the levels of energy generation, cartilage matrix production, and apoptosis induction in HIF-1alpha-deficient chondrocytes under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. In articular cartilages from human OA patients, the expression of HIF-1alpha mRNA was higher in the degenerated regions than in the intact regions. Both IL-1beta and H2O2 accelerated mRNA and protein levels of HIF-1alpha in cultured chondrocytes. Inhibitors for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and p38 kinase caused a significant decrease in catabolic-factor-induced HIF-1alpha expression. HIF-1alpha-deficient chondrocytes did not maintain energy generation and cartilage matrix production under both normoxic and hypoxic conditions. Also, HIF-1alpha-deficient chondrocytes showed an acceleration of catabolic stress-induced apoptosis in vitro. Our findings in human OA cartilage show that HIF-1alpha expression in OA cartilage is associated with the progression of articular cartilage degeneration. Catabolic-stresses, IL-1beta, and oxidative stress induce the expression of HIF-1alpha in chondrocytes. Our results suggest an important role of stress-induced HIF-1alpha in the maintenance of chondrocyte viability in OA articular cartilage.
Figures

Comment in
-
The role of HIF-1alpha in maintaining cartilage homeostasis and during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(1):104. doi: 10.1186/ar1894. Epub 2006 Jan 18. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006. PMID: 16542470 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Catabolic stress induces features of chondrocyte senescence through overexpression of caveolin 1: possible involvement of caveolin 1-induced down-regulation of articular chondrocytes in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Mar;54(3):818-31. doi: 10.1002/art.21639. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16508959
-
Potential involvement of oxidative stress in cartilage senescence and development of osteoarthritis: oxidative stress induces chondrocyte telomere instability and downregulation of chondrocyte function.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(2):R380-91. doi: 10.1186/ar1499. Epub 2005 Jan 26. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15743486 Free PMC article.
-
Water-soluble C60 fullerene prevents degeneration of articular cartilage in osteoarthritis via down-regulation of chondrocyte catabolic activity and inhibition of cartilage degeneration during disease development.Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Oct;56(10):3307-18. doi: 10.1002/art.22917. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. PMID: 17907184
-
Hypoxia and osteoarthritis: how chondrocytes survive hypoxic environments.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007 Sep;19(5):457-62. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e3282ba5693. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17762611 Review.
-
The role of cytokines in osteoarthritis pathophysiology.Biorheology. 2002;39(1-2):237-46. Biorheology. 2002. PMID: 12082286 Review.
Cited by
-
High expression of NDRG3 in osteoarthritis patients.Arthroplasty. 2021 Mar 1;3(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s42836-020-00064-2. Arthroplasty. 2021. PMID: 35236459 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen and reactive oxygen species in articular cartilage: modulators of ionic homeostasis.Pflugers Arch. 2008 Jan;455(4):563-73. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0310-7. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Pflugers Arch. 2008. PMID: 17849146 Review.
-
[Research progress of mechanism of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signaling pathway in condylar cartilage growth and remodeling].Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 1;34(6):639-642. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2016.06.017. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28318168 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Hypoxia Potentiates Anabolic Effects of Exogenous Hyaluronic Acid in Rat Articular Cartilage.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 25;17(7):1013. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071013. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27347945 Free PMC article.
-
New findings in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: therapeutic implications.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2013 Jan;4(1):23-43. doi: 10.1177/2040622312462734. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2013. PMID: 23342245 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

