EID3 is a novel EID family member and an inhibitor of CBP-dependent co-activation
- PMID: 15987788
- PMCID: PMC1159117
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki667
EID3 is a novel EID family member and an inhibitor of CBP-dependent co-activation
Abstract
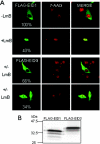
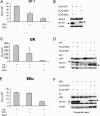
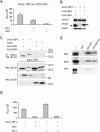
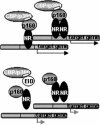
EID1 (E1A-like inhibitor of differentiation 1) functions as an inhibitor of nuclear receptor-dependent gene transcription by directly binding to co-regulators. Alternative targets include the co-repressor small heterodimer partner (SHP, NR0B2) and the co-activators CBP/p300, indicating that EID1 utilizes different inhibitory strategies. Recently, EID2 was characterized as an inhibitor of muscle differentiation and as an antagonist of both CBP/p300 and HDACs. Here, we describe a third family member designated EID3 that is highly expressed in testis and shows homology to a region of EID1 implicated in binding to CBP/p300. We demonstrate that EID3 acts as a potent inhibitor of nuclear receptor transcriptional activity by a mechanism that is independent of direct interactions with nuclear receptors, including SHP. Furthermore, EID3 directly binds to and blocks the SRC-1 interacting domain of CBP, which has been implicated to act as the interaction surface for nuclear receptor co-activators. Consistent with this idea, EID3 prevents recruitment of CBP to a natural nuclear receptor-regulated promoter. Our study suggests that EID-family members EID3 and EID1 act as inhibitors of CBP/p300-dependent transcription in a tissue-specific manner.
Figures


References
-
- Eckner R., Ewen M., Newsome D., Gerdes M., DeCaprio J., Lawrence J., Livingston D. Molecular cloning and functional analysis of the adenovirus E1A-associated 300-kD protein (p300) reveals a protein with properties of a transcriptional adaptor. Genes Dev. 1994;8:869–884. - PubMed
-
- Goodman R.H., Smolik S. CBP/p300 in cell growth, transformation, and development. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1553–1577. - PubMed
-
- Sang N., Caro J., Giordano A. Adenoviral E1A: everlasting tool, versatile applications, continuous contributions and new hypotheses. Front. Biosci. 2002;7:d407–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

