Human microRNA prediction through a probabilistic co-learning model of sequence and structure
- PMID: 15987789
- PMCID: PMC1159118
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki668
Human microRNA prediction through a probabilistic co-learning model of sequence and structure
Abstract
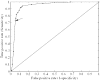
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small regulatory RNAs of approximately 22 nt. Although hundreds of miRNAs have been identified through experimental complementary DNA cloning methods and computational efforts, previous approaches could detect only abundantly expressed miRNAs or close homologs of previously identified miRNAs. Here, we introduce a probabilistic co-learning model for miRNA gene finding, ProMiR, which simultaneously considers the structure and sequence of miRNA precursors (pre-miRNAs). On 5-fold cross-validation with 136 referenced human datasets, the efficiency of the classification shows 73% sensitivity and 96% specificity. When applied to genome screening for novel miRNAs on human chromosomes 16, 17, 18 and 19, ProMiR effectively searches distantly homologous patterns over diverse pre-miRNAs, detecting at least 23 novel miRNA gene candidates. Importantly, the miRNA gene candidates do not demonstrate clear sequence similarity to the known miRNA genes. By quantitative PCR followed by RNA interference against Drosha, we experimentally confirmed that 9 of the 23 representative candidate genes express transcripts that are processed by the miRNA biogenesis enzyme Drosha in HeLa cells, indicating that ProMiR may successfully predict miRNA genes with at least 40% accuracy. Our study suggests that the miRNA gene family may be more abundant than previously anticipated, and confer highly extensive regulatory networks on eukaryotic cells.
Figures





Similar articles
-
MatureBayes: a probabilistic algorithm for identifying the mature miRNA within novel precursors.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 6;5(8):e11843. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011843. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20700506 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide annotation of microRNA primary transcript structures reveals novel regulatory mechanisms.Genome Res. 2015 Sep;25(9):1401-9. doi: 10.1101/gr.193607.115. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 26290535 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA sensitivity to Drosha levels correlates with pre-miRNA secondary structure.RNA. 2014 May;20(5):621-31. doi: 10.1261/rna.043943.113. Epub 2014 Mar 27. RNA. 2014. PMID: 24677349 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the precursor structure in the biogenesis of microRNA.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011 Sep;68(17):2859-71. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0726-2. Epub 2011 May 24. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2011. PMID: 21607569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA stem-loops: to be or not to be cleaved by RNAse III.RNA. 2007 Apr;13(4):457-62. doi: 10.1261/rna.366507. Epub 2007 Feb 13. RNA. 2007. PMID: 17299129 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Profiling Caenorhabditis elegans non-coding RNA expression with a combined microarray.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006 May 31;34(10):2976-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl371. Print 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16738136 Free PMC article.
-
Identifications of conserved 7-mers in 3'-UTRs and microRNAs in Drosophila.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Nov 8;8:432. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-432. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17996040 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide computational identification of functional RNA elements in Trypanosoma brucei.BMC Genomics. 2009 Aug 4;10:355. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-355. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19653906 Free PMC article.
-
Computational prediction of the localization of microRNAs within their pre-miRNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Aug;41(15):7200-11. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt466. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23748953 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA discovery by similarity search to a database of RNA-seq profiles.Front Genet. 2013 Jul 11;4:133. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00133. eCollection 2013. Front Genet. 2013. PMID: 23874353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Kim V.N. Small RNAs: classification, biogenesis, and function. Mol. Cells. 2005;19:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y., Ahn C., Han J., Choi H., Kim J., Yim J., Lee J., Provost P., Radmark O., Kim S., Kim V.N. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature. 2003;425:415–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

