Not all J domains are created equal: implications for the specificity of Hsp40-Hsp70 interactions
- PMID: 15987899
- PMCID: PMC2253343
- DOI: 10.1110/ps.051406805
Not all J domains are created equal: implications for the specificity of Hsp40-Hsp70 interactions
Abstract
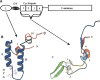
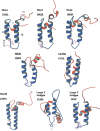
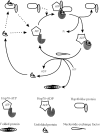
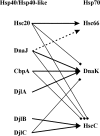
Heat shock protein 40s (Hsp40s) and heat shock protein 70s (Hsp70s) form chaperone partnerships that are key components of cellular chaperone networks involved in facilitating the correct folding of a broad range of client proteins. While the Hsp40 family of proteins is highly diverse with multiple forms occurring in any particular cell or compartment, all its members are characterized by a J domain that directs their interaction with a partner Hsp70. Specific Hsp40-Hsp70 chaperone partnerships have been identified that are dedicated to the correct folding of distinct subsets of client proteins. The elucidation of the mechanism by which these specific Hsp40-Hsp70 partnerships are formed will greatly enhance our understanding of the way in which chaperone pathways are integrated into finely regulated protein folding networks. From in silico analyses, domain swapping and rational protein engineering experiments, evidence has accumulated that indicates that J domains contain key specificity determinants. This review will critically discuss the current understanding of the structural features of J domains that determine the specificity of interaction between Hsp40 proteins and their partner Hsp70s. We also propose a model in which the J domain is able to integrate specificity and chaperone activity.
Figures
References
-
- Berjanskii, M.V., Riley, M.I., Xie, A., Semenchenko, V., Folk, W.R., and Van Doren, S.R. 2000. NMR structure of the N-terminal J domain of murine polyomavirus T antigens. J. Biol. Chem. 275 36094–36103. - PubMed
-
- Berjanskii, M.V., Riley, M.I., and Van Doren, S.R. 2002. Hsc70-interacting HPD loop of the J domain of polyomavirus T antigens fluctuates in ps to ns and μs to ms. J. Mol. Biol. 321 503–516. - PubMed
-
- Bork, P., Sander, C., Valencia, A., and Bukau, B. 1992. A module of the DnaJ heat shock proteins found in malaria parasites. Trends Biochem. Sci. 17 129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

