Loss of histochemical identity in mast cells lacking carboxypeptidase A
- PMID: 15988029
- PMCID: PMC1168831
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.14.6199-6210.2005
Loss of histochemical identity in mast cells lacking carboxypeptidase A
Abstract
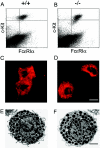
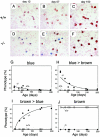
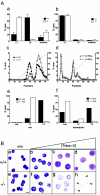
Mast cell carboxypeptidase A (Mc-cpa) is a highly conserved secretory granule protease. The onset of expression in mast cell progenitors and lineage specificity suggest an important role for Mc-cpa in mast cells. To address the function of Mc-cpa, we generated Mc-cpa-null mice. Mc-cpa-/- mast cells lacked carboxypeptidase activity, revealing that Mc-cpa is a nonredundant enzyme. While Mc-cpa-/- peritoneal mast cells were ultrastructurally normal and synthesized normal amounts of heparin, they displayed striking histochemical and biochemical hallmarks of immature mast cells. Wild-type peritoneal mast cells had a mature phenotype characterized by differential histochemical staining with proteoglycan-reactive dyes (cells do not stain with alcian blue but stain with safranin and with berberine) and a high side scatter to forward scatter ratio by flow cytometry and were detergent resistant. In contrast, Mc-cpa-/- peritoneal mast cells, like immature bone marrow-derived cultured mast cells, stained with alcian blue normally or weakly and either did not stain with safranin and berberine or stained weakly, had a low side scatter to forward scatter ratio, and were detergent sensitive. This phenotype was partially ameliorated with age. Thus, histochemistry and flow cytometry, commonly used to measure mast cell maturation, deviated from morphology in Mc-cpa-/- mice. The Mc-cpa-/- mast cell phenotype was not associated with defects in degranulation in vitro or passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in vivo. Collectively, Mc-cpa plays a crucial role for the generation of phenotypically mature mast cells.
Figures




References
-
- Chen, X. J., and L. Enerback. 1999. Immature peritoneal mast cells in neonatal rats express the CTMC phenotype, as well as functional IgE receptors. APMIS 107:957-965. - PubMed
-
- Cool, D. R., E. Normant, F. Shen, H. C. Chen, L. Pannell, Y. Zhang, and Y. P. Loh. 1997. Carboxypeptidase E is a regulated secretory pathway sorting receptor: genetic obliteration leads to endocrine disorders in Cpe(fat) mice. Cell 88:73-83. - PubMed
-
- Dvorak, A. M. 1987. Procedural guide to specimen handling for the ultrastructural pathology service laboratory. J. Electron Microsc. Tech. 6:255-301.
-
- Eklund, K. K., N. Ghildyal, K. F. Austen, D. S. Friend, V. Schiller, and R. L. Stevens. 1994. Mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells (mBMMC) obtained in vitro from mice that are mast cell-deficient in vivo express the same panel of granule proteases as mBMMC and serosal mast cells from their normal littermates. J. Exp. Med. 180:67-73. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
