Identification of a universal Group B streptococcus vaccine by multiple genome screen
- PMID: 15994562
- PMCID: PMC1351092
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1109869
Identification of a universal Group B streptococcus vaccine by multiple genome screen
Erratum in
- Science. 2013 Jan 11;339(6116):141. Nardi Dei, Vincenzo [corrected to Nardi-Dei, Vincenzo]
Abstract
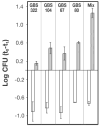
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is a multiserotype bacterial pathogen representing a major cause of life-threatening infections in newborns. To develop a broadly protective vaccine, we analyzed the genome sequences of eight GBS isolates and cloned and tested 312 surface proteins as vaccines. Four proteins elicited protection in mice, and their combination proved highly protective against a large panel of strains, including all circulating serotypes. Protection also correlated with antigen accessibility on the bacterial surface and with the induction of opsonophagocytic antibodies. Multigenome analysis and screening described here represent a powerful strategy for identifying potential vaccine candidates against highly variable pathogens.
Figures
References
-
- Gibbs RS, Schrag S, Schuchat A. Obstet Gynecol. 2004;104:1062. - PubMed
-
- Schuchat A. Lancet. 1999;353:51. - PubMed
-
- More information is available online at www.cdc.gov/ncidod/dbmd/abcs/survreports/gbs02.pdf
-
- Baker CJ, Kasper DL. N Engl J Med. 1976;294:753. - PubMed
-
- Lin FY, et al. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

