Pathogenesis of human metapneumovirus lung infection in BALB/c mice and cotton rats
- PMID: 15994783
- PMCID: PMC1168778
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.14.8894-8903.2005
Pathogenesis of human metapneumovirus lung infection in BALB/c mice and cotton rats
Abstract
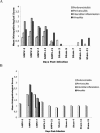
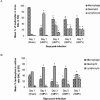
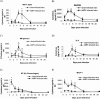
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a newly described member of the Paramyxoviridae family causing acute respiratory tract infections, especially in young children. We studied the pathogenesis of this viral infection in two experimental small animal models (BALB/c mice and cotton rats). Significant viral replication in the lungs of both animals was found following an intranasal challenge of 10(8) 50% tissue culture infectious doses (TCID50) and persisted for <2 and <3 weeks in the case of cotton rats and mice, respectively. Peak viral loads were found on day 5 postinfection in both mice (mean of 1.92 x 10(7) TCID50/g lung) and cotton rats (mean of 1.03 x 10(5) TCID50/g). Clinical symptoms consisting of breathing difficulties, ruffled fur, and weight loss were noted in mice only around the time of peak viral replication. Most significant pulmonary inflammatory changes and peak expression of macrophage inflammatory protein 1alpha, gamma interferon, and RANTES occurred at the time of maximal viral replication (day 5) in both models. Cellular infiltration occurred predominantly around and within alveoli and persisted for at least 21 days in mice, whereas it was more limited in time with more peribronchiolitis in cotton rats. Both animal models would be of great value in evaluating different therapeutic agents, as well as vaccine candidates against hMPV.
Figures
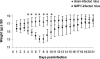
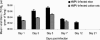


References
-
- Barends, M., L. G. de Rond, J. Dormans, M. van Oosten, A. Boelen, H. J. Neijens, A. D. Osterhaus, and T. G. Kimman. 2004. Respiratory syncytial virus, pneumonia virus of mice, and influenza A virus differently affect respiratory allergy in mice. Clin. Exp. Allergy 34:488-496. - PubMed
-
- Becker, S., J. Quay, and J. Soukup. 1991. Cytokine (tumor necrosis factor, IL-6, and IL-8) production by respiratory syncytial virus-infected human alveolar macrophages. J. Immunol. 147:4307-4312. - PubMed
-
- Biacchesi, S., M. H. Skiadopoulos, G. Boivin, C. T. Hanson, B. R. Murphy, P. L. Collins, and U. J. Buchholz. 2003. Genetic diversity between human metapneumovirus subgroups. Virology 315:1-9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

