Constituents of SH1, a novel lipid-containing virus infecting the halophilic euryarchaeon Haloarcula hispanica
- PMID: 15994804
- PMCID: PMC1168735
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.14.9097-9107.2005
Constituents of SH1, a novel lipid-containing virus infecting the halophilic euryarchaeon Haloarcula hispanica
Abstract
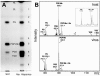
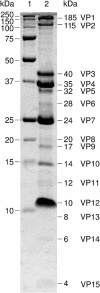
Recent studies have indicated that a number of bacterial and eukaryotic viruses that share a common architectural principle are related, leading to the proposal of an early common ancestor. A prediction of this model would be the discovery of similar viruses that infect archaeal hosts. Our main interest lies in icosahedral double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses with an internal membrane, and we now extend our studies to include viruses infecting archaeal hosts. While the number of sequenced archaeal viruses is increasing, very little sequence similarity has been detected between bacterial and eukaryotic viruses. In this investigation we rigorously show that SH1, an icosahedral dsDNA virus infecting Haloarcula hispanica, possesses lipid structural components that are selectively acquired from the host pool. We also determined the sequence of the 31-kb SH1 genome and positively identified genes for 11 structural proteins, with putative identification of three additional proteins. The SH1 genome is unique and, except for a few open reading frames, shows no detectable similarity to other published sequences, but the overall structure of the SH1 virion and its linear genome with inverted terminal repeats is reminiscent of lipid-containing dsDNA bacteriophages like PRD1.
Figures


References
-
- Abrescia, N. G. A., J. J. Cockburn, J. M. Grimes, G. C. Sutton, J. M. Diprose, S. J. Butcher, S. D. Fuller, C. San Martin, R. M. Burnett, D. I. Stuart, D. H. Bamford, and J. K. H. Bamford. 2004. Insights into assembly from structural analysis of bacteriophage PRD1. Nature 432:68-74. - PubMed
-
- Arnold, H. P., W. Zillig, U. Ziese, I. Holz, M. Crosby, T. Utterback, J. F. Weidmann, J. K. Kristjanson, H. P. Klenk, K. E. Nelson, and C. M. Fraser. 2000. A novel lipothrixvirus, SIFV, of the extremely thermophilic crenarchaeon Sulfolobus. Virology 267:252-266. - PubMed
-
- Baliga, N. S., R. Bonneau, M. T. Facciotti, M. Pan, G. Glusman, E. W. Deutsch, P. Shannon, Y. Chiu, R. S. Weng, R. R. Gan, P. Hung, S. V. Date, E. Marcotte, L. Hood, and W. V. Ng. 2004. Genome sequence of Haloarcula marismortui: a halophilic archaeon from the Dead Sea. Genome Res. 14:2221-2234. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bamford, D. H., and H.-W. Ackermann. 2000. Family Tectiviridae, p. 111-116. In M. H. V. van Regenmortel, C. M. Fauquet, D. H. L. Bishop, E. B. Carstens, M. K. Estes, S. M. Lemon, J. Maniloff, M. A. Mayo, D. J. McGeoch, C. R. Pringle, and R. B. Wickner (ed.), Virus taxonomy: classification and nomenclature of viruses. Seventh report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Academic Press, San Diego, Calif.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

