Radiosensitivity of human colon cancer cell enhanced by immunoliposomal docetaxel
- PMID: 15996023
- PMCID: PMC4502094
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4003
Radiosensitivity of human colon cancer cell enhanced by immunoliposomal docetaxel
Abstract
Aim: To enhance the radiosensitivity of human colon cancer cells by docetaxel.
Methods: Immunoliposomal docetaxel was prepared by coupling monoclonal antibody against carcinoembryonic antigen to cyanuric chloride at the PEG terminus of liposome. LoVo adenocarcinoma cell line was treated with immunoliposomal docetaxel or/and irradiation. MTT colorimetric assay was used to estimate cytotoxicity of immunoliposomal docetaxel and radiotoxicity. Cell cycle redistribution and apoptosis were determined with flow cytometry. Survivin expression in LoVo cells was verified by immunohistochemistry. D801 morphologic analysis system was used to semi-quantify immunohistochemical staining of survivin.
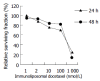
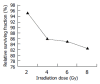
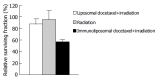
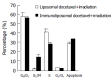
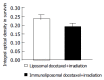
Results: Cytotoxicity was induced by immunoliposomal docetaxel alone in a dose-dependent manner. Immunoli-posomal docetaxel yielded a cytotoxicity effect at a low dose of 2 nmol/L. With a single dose irradiation, the relative surviving fraction of LoVo cells showed a dose-dependent response, but there were no significant changes as radiation delivered from 4 to 8 Gy. Compared with liposomal docetaxel or single dose irradiation, strongly radiopotentiating effects of immunoliposomal docetaxel on LoVo cells were observed. A low dose of immunoliposomal docetaxel could yield sufficient radiosensitivity. Immunoliposomal docetaxel were achieved both specificity of the conjugated antibody and drug radiosensitization. Combined with radiation, immunoliposomal docetaxel significantly increased the percentage of G(2)/M cells and induced apoptosis, but significantly decreased the percentage of cells in G(2)/G(1) and S phase by comparison with liposomal docetaxel. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that the brown stained survivin was mainly in cytoplasm of LoVo cells. Semi-quantitative analysis of the survivin immunostaining showed that the expression of survivin in LoVo cells under irradiation with immunoliposomal docetaxel was significantly decreased.
Conclusion: Immunoliposomal docetaxel is strongly effective for target radiosensitation in LoVo colon carcinoma cells, and may offer the potential to improve local radiotherapy.
Figures

References
-
- Shunyakov L, Ryan CK, Sahasrabudhe DM, Khorana AA. The influence of host response on colorectal cancer prognosis. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2004;4:38–45. - PubMed
-
- Sarid D, Wigler N, Gutkin Z, Merimsky O, Leider-Trejo L, Ron IG. Cutaneous and subcutaneous metastases of rectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2004;9:202–205. - PubMed
-
- Munro AJ, Bentley AH. Deprivation, comorbidity and survival in a cohort of patients with colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl) 2004;13:254–262. - PubMed
-
- Hahnloser D, Haddock MG, Nelson H. Intraoperative radiotherapy in the multimodality approach to colorectal cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2003;12:993–1013, ix. - PubMed
-
- Höcht S, Hammad R, Thiel HJ, Wiegel T, Siegmann A, Willner J, Wust P, Herrmann T, Eble M, Flentje M, et al. Recurrent rectal cancer within the pelvis. A multicenter analysis of 123 patients and recommendations for adjuvant radiotherapy. Strahlenther Onkol. 2004;180:15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

