Bacterial lipopolysaccharide both renders resistant mice susceptible to mercury-induced autoimmunity and exacerbates such autoimmunity in susceptible mice
- PMID: 15996188
- PMCID: PMC1809427
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02849.x
Bacterial lipopolysaccharide both renders resistant mice susceptible to mercury-induced autoimmunity and exacerbates such autoimmunity in susceptible mice
Abstract
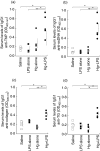
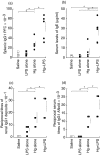
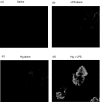
The initiation and severity of systemic autoimmune diseases are influenced by a variety of genetic and environmental factors, in particular bacterial infections and products. Here, we have employed bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which non-specifically activates the immune system, to explore the involvement of innate immunity in mercury-induced autoimmunity in mice. Following treatment of mouse strains resistant [DBA/2 (H-2(d))] or susceptible [SJL(H-2(s))] to such autoimmunity with mercuric chloride and/or LPS or with physiological saline alone (control), their immune/autoimmune responses were monitored. Resistant DBA/2 mice were rendered susceptible to mercury-induced autoimmunity by co-administration of LPS, exhibiting pronounced increases in the synthesis of IgG1 and IgE, high titres of IgG1 deposits in the kidneys and elevated circulating levels of IgG1 antibodies of different specificities. Furthermore, the percentages of the T cells isolated from the spleens of DBA/2 mice exposed to both mercury and LPS that produced pro-inflammatory cytokines were markedly increased by in vitro stimulation with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) and ionomycin, which was not the case for splenic T cells isolated from mice receiving mercuric chloride, LPS or saline alone. In addition, exposure of susceptible SJL mice to mercury in combination with LPS aggravated the characteristic features of mercury-induced autoimmunity, including increased synthesis of IgG1 and IgE, the production of IgG1 anti-nucleolar antibodies (ANolA) and the formation of renal deposits of IgG1. In summary, our findings indicate that activation of the innate immune system plays a key role in both the induction and severity of chemically induced autoimmunity.
Figures

References
-
- Brickman CM, Shoenfeld Y. The mosaic of autoimmunity. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 2001;235:3–15. - PubMed
-
- Luppi P, Rossiello MR, Faas S, Trucco M. Genetic background and environment contribute synergistically to the onset of autoimmune diseases. J Mol Med. 1995;73:381–93. - PubMed
-
- Zandman-Goddard G, Shoenfeld Y. SLE and infections. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2003;25:29–40. - PubMed
-
- Adelman MK, Marchalonis JJ. Endogenous retroviruses in systemic lupus erythematosus: candidate lupus viruses. Clin Immunol. 2002;102:107–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

