Colocalization of endogenous TNF with a functional intracellular splice form of human TNF receptor type 2
- PMID: 15996269
- PMCID: PMC1183239
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-9255-2-7
Colocalization of endogenous TNF with a functional intracellular splice form of human TNF receptor type 2
Abstract
Background: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a pleiotropic cytokine involved in a broad spectrum of inflammatory and immune responses including proliferation, differentiation, and cell death. The biological effects of TNF are mediated via two cell surface TNF receptors: p55TNFR (TNFR1; CD120a) and p75TNFR (TNFR2; CD120b). Soluble forms of these two receptors consisting of the extracellular domains are proteolytically cleaved from the membrane and act as inhibitors. A novel p75TNFR isoform generated by the use of an additional transcriptional start site has been described and was termed hicp75TNFR. We focused on the characterization of this new isoform as this protein may be involved in chronic inflammatory processes.
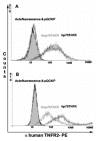
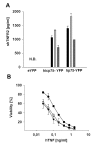
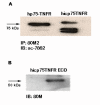
Methods: Cell lines were retroviraly transduced with hp75TNFR isoforms. Subcellular localization and colocalization studies with TNF were performed using fluorescence microscopy including exhaustive photon reassignment software, flow cytometry, and receptosome isolation by magnetic means. Biochemical properties of the hicp75TNFR were determined by affinity chromatography, ELISA, and western blot techniques.
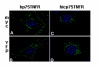
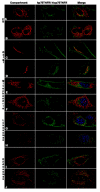
Results: We describe the localization and activation of a differentially spliced and mainly intracellularly expressed isoform of human p75TNFR, termed hicp75TNFR. Expression studies with hicp75TNFR cDNA in different cell types showed the resulting protein mostly retained in the trans-Golgi network and in endosomes and colocalizes with endogenous TNF. Surface expressed hicp75TNFR behaves like hp75TNFR demonstrating susceptibility for TACE-induced shedding and NFkappaB activation after TNF binding.
Conclusion: Our data demonstrate that intracellular hicp75TNFR is not accessible for exogenously provided TNF but colocalizes with endogenously produced TNF. These findings suggest a possible intracellular activation mechanism of hicp75TNFR by endogenous TNF. Subsequent NFkappaB activation might induce anti-apoptotic mechanisms to protect TNF-producing cells from cytotoxic effects of TNF. In addition, the intracellular and not TACE-accessible splice form of the hp75TNFR could serve as a pool of preformed, functional hp75TNFR.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of a novel spliced variant that encodes human soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 2.Int Immunol. 2004 Jan;16(1):169-77. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh014. Int Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14688072
-
Characterization of TNF receptor type 2 isoform in the mouse.Mol Immunol. 2007 Jul;44(14):3563-70. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.03.017. Epub 2007 May 7. Mol Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17485115
-
Differential expression, cytokine modulation, and specific functions of type-1 and type-2 tumor necrosis factor receptors in rat glia.J Neuroimmunol. 1997 May;75(1-2):104-12. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(97)00009-x. J Neuroimmunol. 1997. PMID: 9143243
-
Structural and biological features of the TNF receptor and TNF ligand superfamilies: interactive signals in the pathobiology of Hodgkin's disease.Ann Oncol. 1996;7 Suppl 4:19-26. doi: 10.1093/annonc/7.suppl_4.s19. Ann Oncol. 1996. PMID: 8836404 Review.
-
The Significance of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Type II in CD8+ Regulatory T Cells and CD8+ Effector T Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 22;9:583. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00583. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29623079 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytokine induction of tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 is mediated by STAT3 in colon cancer cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2011 Dec;9(12):1718-31. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0210. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Mol Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21994466 Free PMC article.
-
TNFR1-d2 carrying the p.(Thr79Met) pathogenic variant is a potential novel actor of TNFα/TNFR1 signalling regulation in the pathophysiology of TRAPS.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 18;11(1):4172. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83539-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33603056 Free PMC article.
-
Infection-induced bystander-apoptosis of monocytes is TNF-alpha-mediated.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053589. Epub 2013 Jan 17. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23349721 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative splicing regulation in tumor necrosis factor-mediated inflammation.Oncol Lett. 2017 Nov;14(5):5114-5120. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6905. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 29113151 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis C Virus Exploits Death Receptor 6-mediated Signaling Pathway to Facilitate Viral Propagation.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 25;7(1):6445. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06740-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28743875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith CA, Davis T, Anderson D, Solam L, Beckmann MP, Jerzy R, Dower SK, Cosman D, Goodwin RG. A receptor for tumor necrosis factor defines an unusual family of cellular and viral proteins. Science. 1990;248:1019–1023. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

