The cyclophilins
- PMID: 15998457
- PMCID: PMC1175980
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-7-226
The cyclophilins
Abstract
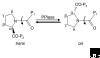
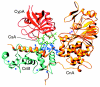
Cyclophilins (Enzyme Commission (EC) number 5.1.2.8) belong to a group of proteins that have peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity; such proteins are collectively known as immunophilins and also include the FK-506-binding proteins and the parvulins. Cyclophilins are found in all cells of all organisms studied, in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes; humans have a total of 16 cyclophilin proteins, Arabidopsis up to 29 and Saccharomyces 8. The first member of the cyclophilins to be identified in mammals, cyclophilin A, is the major cellular target for, and thus mediates the actions of, the immunosuppressive drug cyclosporin A. Cyclophilin A forms a ternary complex with cyclosporin A and the calcium-calmodulin-activated serine/threonine-specific protein phosphatase calcineurin; formation of this complex prevents calcineurin from regulating cytokine gene transcription. Recent studies have implicated a diverse array of additional cellular functions for cyclophilins, including roles as chaperones and in cell signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Fischer G, Bang H, Mech C. Determination of enzymatic catalysis for the cis-trans-isomerization of peptide binding in proline-containing peptides. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1984;43:1101–1111. This paper reports the first identification of a PPIase. - PubMed
-
- Handschumacher RE, Harding MW, Rice J, Drugge RJ, Speicher DW. Cyclophilin: a specific cytosolic binding protein for cyclosporin A. Science. 1984;226:544–547. The first report of cyclophilin A as the cellular receptor for cyclosporin A. - PubMed
-
- Marks AR. Cellular functions of immunophilins. Physiol Rev. 1996;76:631–649. An excellent review on cyclophilin function. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

