Structural genomics of human proteins--target selection and generation of a public catalogue of expression clones
- PMID: 15998469
- PMCID: PMC1250228
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-4-21
Structural genomics of human proteins--target selection and generation of a public catalogue of expression clones
Abstract
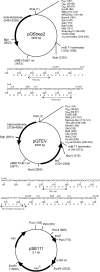
Background: The availability of suitable recombinant protein is still a major bottleneck in protein structure analysis. The Protein Structure Factory, part of the international structural genomics initiative, targets human proteins for structure determination. It has implemented high throughput procedures for all steps from cloning to structure calculation. This article describes the selection of human target proteins for structure analysis, our high throughput cloning strategy, and the expression of human proteins in Escherichia coli host cells.
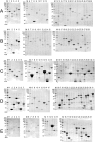
Results and conclusion: Protein expression and sequence data of 1414 E. coli expression clones representing 537 different proteins are presented. 139 human proteins (18%) could be expressed and purified in soluble form and with the expected size. All E. coli expression clones are publicly available to facilitate further functional characterisation of this set of human proteins.
Figures

References
-
- Protein Structure Factory http://www.proteinstrukturfabrik.de
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

