Plasmacytoid predendritic cells initiate psoriasis through interferon-alpha production
- PMID: 15998792
- PMCID: PMC2212894
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20050500
Plasmacytoid predendritic cells initiate psoriasis through interferon-alpha production
Abstract
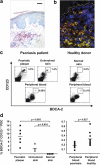
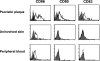
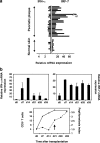
Psoriasis is one of the most common T cell-mediated autoimmune diseases in humans. Although a role for the innate immune system in driving the autoimmune T cell cascade has been proposed, its nature remains elusive. We show that plasmacytoid predendritic cells (PDCs), the natural interferon (IFN)-alpha-producing cells, infiltrate the skin of psoriatic patients and become activated to produce IFN-alpha early during disease formation. In a xenograft model of human psoriasis, we demonstrate that blocking IFN-alpha signaling or inhibiting the ability of PDCs to produce IFN-alpha prevented the T cell-dependent development of psoriasis. Furthermore, IFN-alpha reconstitution experiments demonstrated that PDC-derived IFN-alpha is essential to drive the development of psoriasis in vivo. These findings uncover a novel innate immune pathway for triggering a common human autoimmune disease and suggest that PDCs and PDC-derived IFN-alpha represent potential early targets for the treatment of psoriasis.
Figures

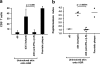
References
-
- Lebwohl, M. 2003. Psoriasis. Lancet. 361:1197–1204. - PubMed
-
- Lew, W., A.M. Bowcock, and J.G. Krueger. 2004. Psoriasis vulgaris: cutaneous lymphoid tissue supports T-cell activation and ‘Type 1’ inflammatory gene expression. Trends Immunol. 25:295–305. - PubMed
-
- Adorini, L., and F. Sinigaglia. 1997. Pathogenesis and immunotherapy of autoimmune diseases. Immunol. Today. 18:209–211. - PubMed
-
- Davidson, A., and B. Diamond. 2001. Autoimmune diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 345:340–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

