Combined effects of GSTP1 and MRP1 in melanoma drug resistance
- PMID: 15999103
- PMCID: PMC2361556
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602681
Combined effects of GSTP1 and MRP1 in melanoma drug resistance
Abstract
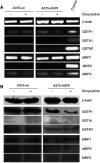
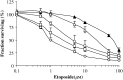
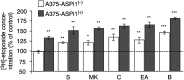
Glutathione-S-transferase Pi1 (GSTP1) and multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) are overexpressed in melanoma, a skin cancer notoriously resistant to all current modalities of cancer therapy. To investigate the involvement of these detoxifying enzymes in the drug resistance of melanoma, an inducible (Tet-On system) antisense (AS) RNA strategy was used to specifically inhibit GSTP1 expression in A375 cells, a human melanoma cell line expressing high levels of GSTP1 and MRP1. Stable transfectant clones were established and analysed for GSTP1 inhibition by AS RNA. The clone A375-ASPi1, presenting a specific 40% inhibition of GSTP1 expression in the presence of doxycycline, was selected. Lowering the GSTP1 level significantly increased (about 3.3-fold) the sensitivity of A375-ASPi1 cells to etoposide. Inhibitors of glutathione synthesis (BSO), GSTs (curcumin, ethacrynic acid), and also of MRPs (MK571, sulphinpyrazone) improved the sensitising effect of GSTP1 AS RNA. All these inhibitors had stronger sensitising effects in control cells expressing high GSTP1 level (A375-ASPi1 cells in the absence of doxycycline). In conclusion, GSTP1 can act in a combined fashion with MRP1 to protect melanoma cells from toxic effects of etoposide.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural requirements for the flavonoid-mediated modulation of glutathione S-transferase P1-1 and GS-X pump activity in MCF7 breast cancer cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 Apr 15;67(8):1607-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2003.12.032. Biochem Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15041478
-
The influence of coordinate overexpression of glutathione phase II detoxification gene products on drug resistance.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Aug;294(2):480-7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. PMID: 10900222
-
Inhibition of glutathione S-transferase activity in human melanoma cells by alpha,beta-unsaturated carbonyl derivatives. Effects of acrolein, cinnamaldehyde, citral, crotonaldehyde, curcumin, ethacrynic acid, and trans-2-hexenal.Chem Biol Interact. 1996 Oct 21;102(2):117-32. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(96)03739-8. Chem Biol Interact. 1996. PMID: 8950226
-
Pi-class glutathione S-transferase: regulation and function.Chem Biol Interact. 1998 Apr 24;111-112:69-82. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(97)00176-2. Chem Biol Interact. 1998. PMID: 9679544 Review.
-
Glutathione Transferase P1: Potential Therapeutic Target in Ovarian Cancer.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Nov 16;58(11):1660. doi: 10.3390/medicina58111660. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36422199 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sirtuin 3 enhanced drug sensitivity of human hepatoma cells through glutathione S-transferase pi 1/JNK signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 2;7(31):50117-50130. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10319. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27367026 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical relevance of neutral endopeptidase (NEP/CD10) in melanoma.J Transl Med. 2007 Jan 5;5:2. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-5-2. J Transl Med. 2007. PMID: 17207277 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacogenomics approach reveals MRP1 (ABCC1)-mediated resistance to geldanamycins.Pharm Res. 2009 Apr;26(4):936-45. doi: 10.1007/s11095-008-9796-8. Epub 2008 Dec 10. Pharm Res. 2009. PMID: 19067123
-
Glutathione in cancer cell death.Cancers (Basel). 2011 Mar 11;3(1):1285-310. doi: 10.3390/cancers3011285. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 24212662 Free PMC article.
-
RNA interference-mediated knockdown of SIRT1 and/or SIRT2 in melanoma: Identification of downstream targets by large-scale proteomics analysis.J Proteomics. 2018 Jan 6;170:99-109. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Sep 5. J Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 28882678 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey HH (1998) -S,R-buthionine sulfoximine: historical development and clinical issues. Chem Biol Interact 111–112: 239–254 - PubMed
-
- Ban N, Takahashi Y, Takayama T, Kura T, Katahira T, Sakamaki S, Niitsu Y (1996) Transfection of glutathione S-transferase (GST)-pi antisense complementary DNA increases the sensitivity of a colon cancer cell line to adriamycin, cisplatin, melphalan, and etoposide. Cancer Res 56: 3577–3582 - PubMed
-
- Borst P, Evers R, Kool M, Wijnholds J (1999) The multidrug resistance protein family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1461: 347–357 - PubMed
-
- Cole SP, Bhardwaj G, Gerlach JH, Mackie JE, Grant CE, Almquist KC, Stewart AJ, Kurz EU, Duncan AM, Deeley RG (1992) Overexpression of a transporter gene in a multidrug-resistant human lung cancer cell line. Science 258: 1650–1654 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

